China is one of the largest global hubs for CNC machining, offering a wide range of precision manufacturing services with competitive pricing and mature supply chains. This guide explains, in a structured and technical way, how China CNC machining services work, what capabilities are available, how to specify your parts correctly, and how to select and manage suppliers for reliable results.
What Is CNC Machining and Why Source in China
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a subtractive manufacturing process where pre-programmed computer software controls machine tools to produce precise parts from solid material. The most common CNC operations are milling, turning, drilling, boring, tapping and grinding.
China has developed extensive CNC machining capabilities spanning prototype, small batch, and mass production. Many buyers choose Chinese machine shops for:
- Broad range of machine types and processes under one roof
- Competitive machining and material costs
- Experience with export projects in automotive, machinery, electronics and consumer products
- Access to additional processes such as casting, forging and surface finishing within the same region
For engineering teams, China is often suitable for rapid prototypes, functional samples, pilot runs and large-scale production of machined metal and plastic components.
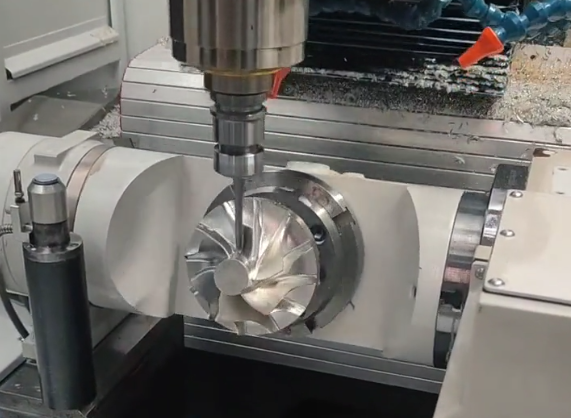

Common CNC Machining Processes in China
Chinese machine shops usually operate multiple kinds of CNC machines. Understanding the main processes helps you match your design to the right capability.
CNC Milling
CNC milling uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece that is fixed to a table or held in fixtures. Chinese factories widely use 3-axis, 4-axis and 5-axis machining centers.
Typical characteristics:
- Suitable for prismatic parts, complex 3D surfaces, housings, brackets and plates
- Supports a large variety of metals and plastics
- Good for both prototypes and production runs
Common parameters for standard Chinese CNC milling centers (values are indicative and vary by shop):
| Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Number of axes | 3-axis, 3+2, 4-axis, 5-axis |
| Max X travel | 500 mm to 2,000 mm |
| Max Y travel | 400 mm to 1,000 mm |
| Max Z travel | 300 mm to 1,000 mm |
| Spindle speed | 6,000 to 24,000 rpm |
| Positioning accuracy | ±0.005 mm to ±0.02 mm |
| Repeatability | ±0.003 mm to ±0.01 mm |
CNC Turning (Lathe Machining)
CNC turning uses a rotating workpiece and a stationary cutting tool to create cylindrical and rotational parts such as shafts, bushings, pins and threaded components. Many Chinese shops also have turn-mill centers combining turning and milling in one setup.
Typical characteristics:
- Efficient for round parts and high-volume production
- Supports internal and external turning, threading, grooving and drilling
- Turning centers with live tooling can add milled features, flats and slots
Indicative capability ranges:
| Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Max turning diameter | 10 mm to 500 mm (larger on heavy lathes) |
| Max turning length | 20 mm to 1,500 mm |
| Chuck size | 4" to 15" |
| Spindle speed | 1,500 to 6,000 rpm |
| Positioning accuracy | ±0.005 mm to ±0.02 mm |
Multi-Axis and Complex Machining
For parts requiring intricate geometries, undercuts or multi-face machining in one setup, Chinese suppliers frequently use:
- 4-axis rotary tables for indexing or continuous rotation
- 5-axis simultaneous machining centers for freeform surfaces
- Turn-mill centers for parts needing both turning and complex milling
These setups reduce fixture changes, improve accuracy between features and shorten lead times for complex components.
Supplementary Machining Operations
Beyond milling and turning, China CNC machining services often include additional operations:
Drilling and tapping: Creation of through-holes, blind holes, and threaded holes (metric and imperial) using CNC or dedicated drilling/tapping machines.
Grinding: Surface and cylindrical grinding to achieve tight flatness and roundness tolerances, low surface roughness and precise fits.
Electrical discharge machining (EDM): Wire-cut EDM and sinker EDM for hard materials and detailed internal features that are difficult or impossible to machine conventionally.

Materials Used in China CNC Machining
China’s machining ecosystem supports a wide selection of metals and plastics, with ready access to raw material stock and local mills. When requesting quotes, specify material grade standards clearly (e.g., ASTM, EN, JIS, GB) to avoid confusion.
Common Metal Materials
Typical metals available from Chinese CNC shops include:
Aluminum alloys: Widely used for their machinability, lightweight and good strength-to-weight ratio. Common grades:
- Aluminum 6061-T6: General-purpose structural alloy, good balance of strength, corrosion resistance and cost
- Aluminum 6082, 6063: Used in structural and extrusion applications
- Aluminum 7075-T6: High-strength aerospace-grade aluminum, less corrosion resistant than 6061
- Aluminum 2024: High strength and fatigue resistance for aerospace and performance components
Carbon and alloy steels: Used for structural, mechanical and tooling parts.
- Mild steels: Q235, Q345, A36; suitable for general structural components
- Medium carbon steels: 1045, 45#, used for shafts, gears and mechanical parts
- Alloy steels: 4130, 4140, 4340, 40Cr; suitable for high-strength applications and often heat-treated
Stainless steels: Used when corrosion resistance is important.
- 304 / 1.4301: Very common, good corrosion resistance, good weldability
- 316 / 1.4401: Better corrosion and chemical resistance, suitable for marine and chemical environments
- 303: Free-machining stainless steel for improved machinability and surface finish
- 17-4PH: Precipitation hardening stainless offering high strength and hardness after heat treatment
Copper and copper alloys:
- Brass: Good machinability, used for fittings, decorative components and connectors
- Copper: High electrical and thermal conductivity for electrical and heat transfer applications
- Bronze: Used for bushings, bearings and wear components
Other metals: Some Chinese shops also support titanium alloys (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V) and tool steels (e.g., D2, H13, SKD11) requiring more advanced machining setups and careful tooling.
Plastics and Engineering Polymers
China CNC machining services also cover a broad range of plastics, particularly for functional prototypes, low-volume housings, and non-metallic functional parts.
Common plastics include:
- ABS: Good impact strength, widely used in enclosures and consumer products
- PC (polycarbonate): High impact resistance and transparency, used in optical and protective parts
- PP (polypropylene): Chemical resistance and fatigue resistance (hinges, clips)
- POM (acetal, Delrin): Excellent dimensional stability and low friction, suitable for gears and precision parts
- Nylon (PA6, PA66): Good mechanical strength, used for bearings, gears, structural components
- PEEK: High performance engineering plastic for high temperature and chemically demanding environments
When machining plastics, Chinese shops often adjust cutting parameters to avoid heat build-up, deformation or stress cracking.
Typical Tolerances and Surface Roughness
Precision is a core parameter when sourcing CNC parts. Chinese machining suppliers can achieve tight tolerances if the design and quality expectations are specified clearly.
Dimensional Tolerances
Standard machining tolerances for many general mechanical parts are often in the range of ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm, depending on size and function. With suitable machines, tooling and process control, much tighter tolerances are possible on critical features.
Typical achievable tolerances (indicative, subject to part geometry and material):
- General features: ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm
- Precision features (e.g., bearing fits, critical bores): ±0.01 mm to ±0.02 mm
- High precision (select shops with dedicated equipment): ±0.005 mm and below on selected dimensions
To minimize issues, define:
- Critical dimensions and fits (e.g., H7/g6)
- Geometric tolerances (flatness, parallelism, concentricity and runout) on key surfaces
- Tolerance zones based on functional needs, not tighter than necessary
Surface Roughness
Surface roughness is commonly expressed as Ra (arithmetical mean roughness). China CNC machining services can produce different surface finishes depending on tooling, cutting parameters and secondary finishing operations.
Typical machining roughness ranges:
- Standard milled surface: Ra 1.6 to 3.2 μm
- Fine machining with optimized parameters: Ra 0.8 to 1.6 μm
- Ground surfaces: Ra 0.2 to 0.8 μm
When requesting quotes, specify any special surface finish or roughness requirements, particularly for sealing surfaces, sliding surfaces, optical or decorative areas.
Surface Finishing and Post-Processing in China
Beyond raw machined surfaces, China CNC machining suppliers routinely provide in-house or outsourced finishing services. This simplifies logistics and allows you to receive finished parts ready for assembly.
Mechanical Finishing
Mechanical processes modify the surface geometrically or improve appearance:
- Deburring and edge rounding: Removal of burrs and sharp edges through manual tools, tumbling or brushing
- Polishing and buffing: For improved appearance and lower surface roughness
- Bead blasting or sandblasting: Uniform matte finish, removal of machining lines
Chemical and Electrochemical Finishing
Commonly used treatments include:
- Anodizing (Type II, Type III) for aluminum: Provides corrosion resistance, surface hardness and color options
- Conversion coatings (e.g., chromate) on aluminum or zinc-plated parts
- Electroplating (nickel, chrome, zinc): Corrosion protection and cosmetic finishes for steel and other metals
- Passivation for stainless steel: Enhances corrosion resistance by removing contaminants
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment modifies mechanical properties such as hardness, strength and toughness. In China, typical heat treatments include:
- Quenching and tempering for carbon steels and alloy steels
- Carburizing and nitriding for wear-resistant surfaces
- Solution treatment and aging for precipitation hardening steels and aluminum alloys
When heat treatment is required, specify the hardness range, standard (e.g., HRC, HBW) and areas requiring hardness or case depth.
Design for Manufacturability for China CNC Machining
Proper design for manufacturability (DFM) helps reduce cost, improve consistency and minimize issues when working with Chinese CNC machining suppliers. Clear, realistic specifications and workable geometries are essential.
Wall Thickness and Feature Size
Very thin walls and extremely small features increase production difficulty and risk of deformation. Common guidelines:
- Minimum wall thickness for metals: 0.5 to 1.0 mm depending on material and geometry
- Minimum wall thickness for plastics: 1.0 to 1.5 mm for stability and to avoid warpage
- Minimum hole diameter: Typically 1.0 mm for standard drills; smaller holes may require specialized tools
Corner Radii and Internal Features
Internal corners created by milling tools will always have a radius. To simplify machining and reduce tool wear:
- Use standard tool radii when possible (e.g., 1, 2, 3 mm)
- Avoid extremely deep, narrow pockets that are difficult to reach
- Add relief or open pockets where tight internal corners are not functionally required
Tolerances and GD&T
Overly tight tolerances significantly increase machining time, inspection effort and rejection rate. When working with Chinese suppliers:
- Apply tight tolerances only where functionally necessary
- Use general tolerance notes for non-critical dimensions (e.g., ISO 2768-m)
- Communicate GD&T symbols clearly and avoid ambiguous or conflicting tolerances
Drawings and 3D Models
Provide both 3D CAD models (e.g., STEP, IGES, Parasolid) and 2D drawings with critical dimensions, tolerances, material specification and finish requirements. In many Chinese shops:
- The 3D model is used for CAM programming and toolpath generation
- The 2D drawing acts as the official reference for dimensions and tolerances
To prevent misinterpretation, ensure consistency between the 3D model and 2D drawing and clearly mark any dimensions that supersede the model.
Quotation and Cost Structure for China CNC Machining Services
Understanding how Chinese machining suppliers calculate cost helps you estimate budgets and optimize designs.
Cost Components
Typical cost elements include:
- Raw material cost: Depends on material type, grade, dimensions and market price
- Machining time: Determined by part complexity, tolerances, required setup and machine type
- Setup and programming: CAM programming, fixture design and setup, especially for new parts or complex geometries
- Tooling and consumables: Cutting tools, inserts, fixtures, jigs and their wear
- Surface finishing and heat treatment: Additional processes beyond machining
- Inspection and quality documentation: Extra checks, reports or certifications if required
- Packaging and logistics: Protective packaging, labeling and transport to port or directly to your destination
Factors Affecting Machining Price
From a sourcing perspective, some key factors influencing the total cost are:
- Part complexity: Number of operations, setups and required axes
- Tolerances and quality requirements: Tighter tolerances often mean slower machining and more inspection
- Order quantity: Higher volumes distribute setup costs over more units
- Material machinability: Harder or gummier materials require slower cutting and specialized tooling
- Surface and cosmetic requirements: Fine finishes and decorative treatments add process steps
To obtain accurate quotes, share 3D/2D data, material, quantity, finishing requirements and any special testing or certification needs.
Lead Times and Production Volumes
China CNC machining services can accommodate a wide range of lead time and volume requirements, from rapid prototypes to long-term serial production.
Prototyping and Low Volume Production
For prototypes and small batches, many Chinese suppliers offer flexible capacity and quick turnaround:
- Lead time for prototypes: Often 3 to 10 working days after design confirmation
- Low volume runs: Tens to hundreds of parts, depending on complexity
- Rapid iteration: Changes between batches are easier to accommodate
Mass Production
For larger runs, Chinese machining shops may:
- Invest in dedicated fixtures and optimized tooling
- Standardize process parameters and inspection routines
- Set up multi-machine production cells
Lead times for mass production depend on capacity and part complexity but usually include a sample approval stage (first article samples) before full-scale production.
Quality Control Practices in Chinese CNC Shops
Quality management is central to reliable CNC machining. Many Chinese suppliers serving international markets operate under ISO 9001 and industry-specific standards. When assessing a supplier, understanding their quality control infrastructure is important.
Incoming, In-Process and Final Inspection
Quality control typically consists of:
- Incoming inspection: Verification of raw material certificates, dimensions and properties
- In-process inspection: First article inspection at each setup and periodic checks during production
- Final inspection: Dimensional and visual checks, documentation and packaging inspection before shipment
Measurement Equipment
Common measuring tools in Chinese CNC machine shops include:
- Basic tools: Vernier calipers, micrometers, height gauges, bore gauges
- Surface roughness testers: For measuring Ra or other roughness parameters
- CMM (coordinate measuring machines): For complex geometries and GD&T requirements
- Optical projectors and vision measuring systems: For small, intricate or delicate parts
Ask suppliers for their equipment list and calibration practices, particularly when parts require tight tolerances or critical geometric features.
Documentation and Traceability
For industries that demand traceability, Chinese CNC machining services can provide:
- Material certificates (e.g., mill certificates, composition reports)
- Heat treatment certificates
- Dimensional inspection reports or full inspection data for critical features
- Serial numbers or batch markings on parts or packaging
Define documentation requirements clearly at the quotation stage so the supplier can plan resources accordingly.
Selecting a China CNC Machining Supplier
Selecting the right supplier in China is a combination of evaluating technical capability, quality systems, communication and business stability. A structured selection process reduces risk and improves long-term cooperation.
Technical Capability Assessment
Key aspects include:
- Machine list and capacities (types, brands, axes, travel ranges)
- Supported materials and grades
- Experience with similar parts or industries
- In-house vs. outsourced processes (e.g., surface finishing, heat treatment)
Request sample projects, photos or sample parts to confirm their ability to handle your geometry and tolerance requirements.
Quality Management and Certifications
Confirm the supplier’s quality system status:
- ISO 9001 certification and scope
- Internal procedures for calibration, nonconforming product handling and corrective actions
- Availability of CMM and other precision inspection equipment for critical parts
If parts are used in regulated sectors, check for relevant certifications or experience (e.g., automotive, medical device components under a larger OEM’s quality system).
Communication and Engineering Support
Efficient collaboration with Chinese machining suppliers relies on clear communication and engineering feedback:
- Ability to understand and work with English-language drawings and standards
- Responsiveness during quotation and engineering clarification
- DFM feedback capability to suggest modifications for better manufacturability
Establish direct contacts for engineering, quality and sales to handle issues quickly.
Site Visits and Audits
When possible, visiting the factory or commissioning a third-party audit provides a realistic view of the supplier’s operations, cleanliness, workflow, and quality discipline. Even a virtual tour or live video walkthrough can be useful for remote assessments.
Ordering Workflow for China CNC Machining
A typical workflow for outsourcing CNC machining to China follows a sequence of steps from RFQ to shipment.
1) Request for Quotation (RFQ)
Prepare and send the following information:
- 3D CAD models and 2D drawings with material, tolerances and finishes
- Quantities per order or per year
- Special requirements (e.g., inspection reports, certifications, packaging)
- Required incoterms (e.g., EXW, FOB, CIF) and delivery location
The supplier will evaluate machining time, material, setup, finishing and logistics to prepare a quote.
2) DFM Review and Clarification
After receiving a quotation and before sample production, conduct a design for manufacturability review:
- Clarify ambiguous dimensions or tolerances
- Discuss potential design changes to reduce cost or risk
- Confirm surface finish requirements and cosmetic standards
Any agreed changes should be reflected in updated drawings or models.
3) Sample Production and First Article Inspection
Most projects start with a sample or first article stage:
- Supplier produces samples according to the latest drawings
- First article inspection (FAI) is performed and measurement reports are shared
- Customer checks dimensional accuracy, fit, function and appearance
Feedback from this stage may lead to minor adjustments in design or process parameters before mass production.
4) Mass Production and Ongoing Quality Assurance
Once samples are approved and purchase orders are confirmed, full production begins:
- Production schedules and batch sizes are planned
- In-process and final inspections monitor quality
- Periodic requalification of parts may be done if tools, fixtures or processes change
5) Packaging, Logistics and Shipping
Packaging must protect parts during long-distance transportation and storage. Common practices include:
- Individual wrapping for sensitive or cosmetic parts
- Anti-rust oil or VCI (volatile corrosion inhibitor) packaging for steel parts
- Labels with part numbers, quantities and batch information
Logistics can be arranged by the supplier or by the buyer using their own forwarder, with common options such as air freight for urgent small batches and sea freight for larger volumes.
Issues and Practical Considerations
Working with CNC machining suppliers in China offers many advantages, but certain practical considerations must be managed for smooth collaboration.
Engineering Clarification and Tolerance Interpretation
Differences in engineering standards or interpretation can lead to misunderstandings. Points to consider:
- Specify standards used on drawings (e.g., ISO, ASME) and units (mm or inch)
- Clarify any general note such as unspecified tolerance ranges
- Share reference samples or photos for cosmetic expectations when important
Material Equivalence and Standards
Local Chinese material standards (e.g., GB) may differ from ASTM or EN standards. To avoid mismatching materials:
- Provide exact material designations and preferred international standards
- Request material certificates showing chemical composition and mechanical properties
- Confirm any acceptable equivalent grades in writing
Dimensional Consistency Across Batches
For recurring orders, dimensional consistency is important:
- Maintain a master drawing revision and manage changes systematically
- Agree on a control plan and sampling frequency for critical dimensions
- Archive sample parts and inspection records as references
Industry Applications of China CNC Machining
China CNC machining services support many industries by providing precise metal and plastic parts. Common application areas include:
- Automotive: Housings, brackets, shafts, flanges, engine components, tooling
- Industrial machinery: Gears, couplings, machine frames, custom fixtures
- Electronics: Heat sinks, enclosures, connector housings and mechanical supports
- Medical and laboratory equipment: Machined metal and plastic components for devices, fixtures and instruments
- Aerospace and UAVs: Structural components, brackets and precision mechanical parts
- Consumer products: Custom hardware, bicycle parts, sports equipment components
By combining CNC machining with other processes like casting, forging and injection molding, Chinese suppliers can support complete product mechanical structures from prototype to production.
How to Prepare Effective RFQs for China CNC Machining
Well-prepared RFQs reduce back-and-forth communication and lead to more accurate quotations and better outcomes.
Essential Information to Include
- 3D model (STEP, IGES, Parasolid) and 2D drawing (PDF, DWG, DXF)
- Material grade and standard
- Quantity per batch and annual quantity estimate
- Tolerances and surface roughness requirements
- Surface finishing and heat treatment requirements
- Inspection requirements and documentation needs
- Target lead time and delivery terms
Prioritizing Requirements
Help suppliers understand trade-offs by clarifying what aspects are most important for each part:
- Functional dimensions vs. aesthetic features
- Critical tolerances vs. general dimensions
- Cost targets vs. lead time constraints
This allows suppliers to suggest alternative processes, materials or tolerances where appropriate.
Risk Mitigation and Long-Term Cooperation
Developing stable, long-term relationships with Chinese CNC machining suppliers reduces total cost over time and supports more complex projects.
Starting with Pilot Orders
To validate capability and communication, many buyers begin with pilot orders:
- Start with a limited number of part types or a subset of your BOM
- Evaluate quality, communication, on-time delivery and documentation
- Gradually increase order volumes and part complexity after successful runs
Supplier Performance Monitoring
Track key performance indicators such as:
- On-time delivery rate
- Nonconformance rate and rework frequency
- Response time to engineering queries and corrective actions
Regular reviews help both parties improve process capability and coordination.
Conclusion
China CNC machining services provide extensive capabilities for precision metal and plastic components, from prototypes through to high-volume production. By understanding available processes, material options, typical tolerances, finishing possibilities, cost drivers and quality practices, buyers can design manufacturable parts, prepare clear RFQs and select suitable suppliers.
Systematic communication, accurate technical documentation and well-defined quality expectations are essential to leverage the full potential of Chinese CNC machining while maintaining dimensional accuracy, consistency and cost efficiency.
FAQ
What are China CNC machining services?
China CNC machining services refer to precision manufacturing services provided by CNC machine shops in China, including milling, turning, drilling, and multi-axis machining for custom metal and plastic parts.
Why choose China for CNC machining?
China offers competitive pricing, advanced CNC equipment, skilled machinists, and scalable production capacity. This makes China an ideal choice for prototyping, low-volume, and high-volume CNC machining projects.
What is the typical lead time for CNC machining in China?
Lead time varies by part complexity and quantity. Prototypes usually take 3–7 working days, while production orders may take 1–4 weeks.
Is communication a concern when working with China CNC machining suppliers?
Reputable suppliers provide English-speaking sales and engineering support, clear documentation, and regular production updates to ensure smooth communication.
How do I choose a reliable CNC machining supplier in China?
Look for experience, certifications (such as ISO 9001), quality control processes, material traceability, sample approval procedures, and positive customer references.


