Precision CNC machining in China provides high-accuracy, repeatable manufacturing for metal and plastic parts across aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, robotics, and industrial equipment applications. This guide explains key CNC processes, machinable materials, tolerance capabilities, quality standards, and how to work effectively with Chinese CNC suppliers for small batches and medium-to-high volume production.
Overview of Precision CNC Machining in China
Precision CNC machining uses computer-controlled cutting tools on multi-axis machines to remove material and produce components that meet strict dimensional and geometric requirements. Chinese machining shops combine modern equipment, CAM programming, and standardized inspection methods to deliver parts from prototypes to mass production batches.
Typical applications include:
- Functional prototypes and pilot runs for mechanical assemblies
- High-precision fixtures, jigs, and tooling components
- Complex housings and structural parts for electronics and machinery
- Shafts, bushings, gears, and bearing components for motion systems
Many Chinese CNC suppliers support integrated services such as material sourcing, heat treatment, surface finishing, assembly, and packaging, enabling one-stop solutions for international buyers.
Core CNC Processes Used in China
Chinese precision machining facilities commonly integrate multiple CNC processes in one facility to optimize lead time, cost, and accuracy. Understanding each process helps in selecting appropriate manufacturing routes for specific part geometries and tolerances.
CNC Milling
CNC milling removes material with rotating cutting tools, suitable for prismatic parts and complex 3D surfaces. Chinese workshops typically operate 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis vertical and horizontal machining centers.
Main milling capabilities include:
- Face milling, contouring, pocketing, and slotting
- 3D surface machining for molds, dies, and complex covers
- Multi-face machining in one setup using rotary tables or 4/5-axis machines
Common spindle speed ranges: 6,000–24,000 rpm depending on machine class and material; tool holders include BT, CAT, and HSK systems. High-speed machining is used for aluminum and plastics to achieve fine surface finish and efficient material removal.
CNC Turning and Turn-Milling
CNC turning is used for rotationally symmetric parts such as shafts, bushings, couplings, and threaded components. Many Chinese factories operate both standard CNC lathes and turn-mill centers.
Typical capabilities:
- External and internal turning, facing, grooving, threading, and boring
- Live tooling for cross drilling, milling flats, and light slotting
- Bar feeding for medium-to-high volume production of small parts
Turn-mill centers combine turning and milling operations in one machine, reducing setups and improving concentricity and positional accuracy between features.
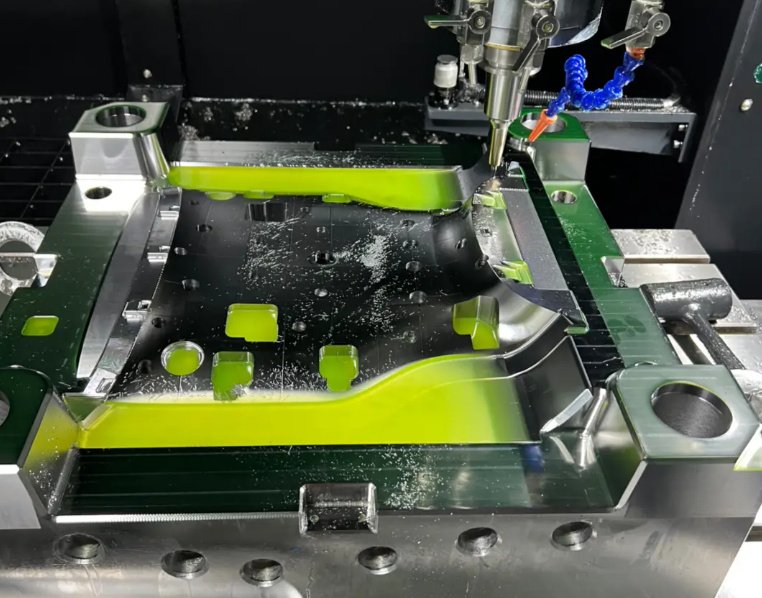
5-Axis and Multi-Axis Machining
5-axis CNC machining is widely used in China for parts that require multiple angled features, complex contours, and high dimensional accuracy with fewer setups. This is common in aerospace components, medical devices, optical housings, and intricate automotive parts.
Capabilities include:
Simultaneous 5-axis contouring and indexed 5-axis machining, improved access to deep cavities, reduced fixture complexity, and enhanced geometric consistency across multiple features in a single clamping.
EDM and Wire EDM
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) and Wire EDM are used to create tight-tolerance features in hard materials or intricate shapes that are difficult to machine using conventional cutting tools.
Main uses:
Fine details, sharp internal corners, narrow slots, small holes, and hardened steel inserts for molds and tooling. Wire EDM is particularly suited for high-precision profile cutting and complex 2D and 2.5D geometries.
Grinding and Superfinishing
For components that require very tight dimensional tolerances and fine surface finishes, precision grinding is frequently applied after CNC milling or turning.
Common grinding operations include:
Surface grinding, cylindrical grinding, centerless grinding, and internal grinding, often combined with lapping and honing where sub-micron accuracy and low surface roughness are required.
Materials for Precision CNC Machining in China
Chinese CNC shops work with a wide range of metals and plastics sourced from domestic and international mills. Material selection depends on mechanical performance, corrosion resistance, machinability, and cost.
| Material Type | Typical Grades | Key Properties | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | AL 6061, 6082, 7075, 2024, 5052 | Lightweight, good machinability, good strength-to-weight ratio, good anodizing response | Housings, fixtures, panels, heat sinks, structural parts |
| Stainless Steel | SS 304, 316/316L, 303, 410, 420, 17-4PH | Corrosion resistance, higher strength, good for harsh environments and food/medical applications | Medical devices, food processing parts, marine components, fasteners |
| Carbon & Alloy Steel | 1018, 1020, 1045, 4140, 4340, 40Cr, 20CrMnTi | High strength, hardenability after heat treatment, good fatigue properties | Gears, shafts, mechanical components, automotive parts |
| Copper & Brass | H62, C3604, C110, C122, CuZn39Pb3 | Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, good machinability in brasses | Connectors, terminals, electrical components, plumbing parts |
| Tool Steel | D2, SKD11, H13, P20, O1, S7 | High hardness, wear resistance, stable during heat treatment | Molds, dies, cutting tools, wear plates |
| Titanium Alloys | TC4 / Ti-6Al-4V, TA2 (Grade 2) | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility | Medical implants, aerospace components, high-end sports equipment |
| Engineering Plastics | POM (Delrin), PA (Nylon), PC, ABS, PEEK, PTFE, UHMW-PE | Low weight, chemical resistance, electrical insulation, low friction | Insulators, bushings, guides, spacers, low-load structural parts |
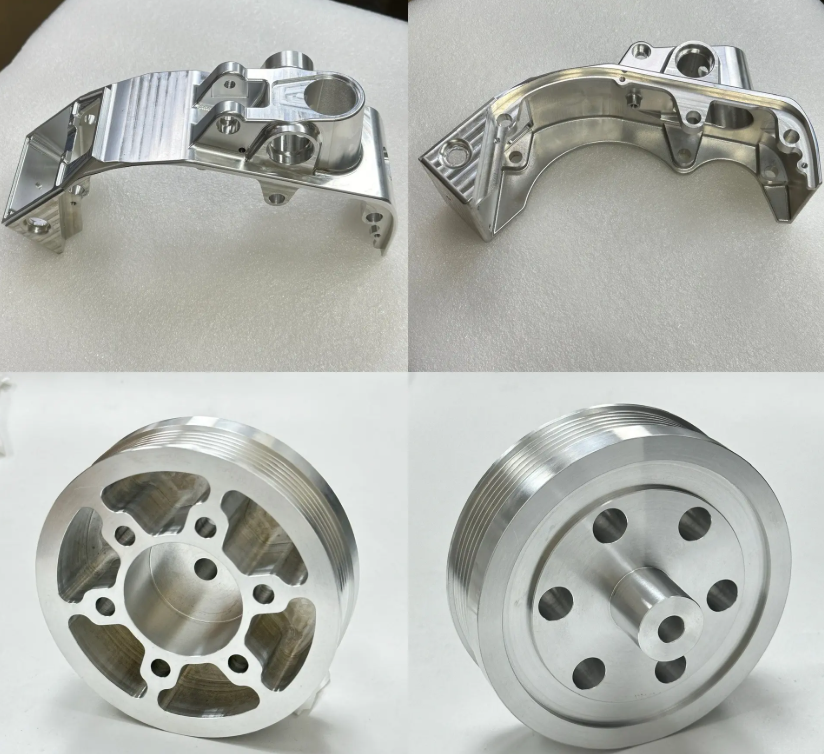

Metal Material Considerations
For metals, Chinese suppliers generally offer mill certificates (such as EN 10204 3.1) and can perform third-party testing if requested. When specifying materials, buyers should clearly indicate international equivalents (e.g., aluminum 6061-T6, stainless steel 316L) to avoid confusion with localized grade naming.
Heat treatment processes, such as quenching and tempering, nitriding, carburizing, and solution aging, are commonly performed to achieve target hardness and mechanical performance.
Engineering Plastics and Composite Materials
Engineering plastics are widely machined for low-weight and electrically insulating components. Chinese shops apply specific cutting parameters and tool geometries to control burrs, deformation from heat, and dimensional stability.
For high-performance polymers like PEEK and PTFE, stable fixturing, sharp tools, and controlled cutting speeds are essential to maintain dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
Precision and Tolerance Capabilities
Precision CNC machining in China can achieve tight dimensional tolerances when supported by appropriate machine tools, cutting tools, process control, and inspection methods. Tolerance ranges depend on part size, geometry, material, and manufacturing process.
| Feature Type | Typical Tolerance Range | Common Surface Roughness (Ra) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard milled dimensions | ±0.05 mm to ±0.10 mm | 1.6–3.2 μm (after milling) |
| High-precision milled features | ±0.01 mm to ±0.02 mm | 0.8–1.6 μm (with finishing pass) |
| Standard turned diameters | ±0.02 mm to ±0.05 mm | 1.6–3.2 μm (after turning) |
| Ground diameters and surfaces | ±0.002 mm to ±0.01 mm | 0.1–0.8 μm (after grinding) |
| Hole diameters (drilled & reamed) | H7–H9 fits commonly; down to ±0.005 mm when controlled | 0.8–3.2 μm depending on finishing |
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) is widely used for form, orientation, and position control. Chinese machining suppliers can work from drawings with GD&T symbols (parallelism, perpendicularity, true position, circularity, runout, flatness) in accordance with ISO or ASME standards.
Factors Influencing Achievable Tolerances
Achievable tolerances are determined by several key factors:
Machine tool precision, tool selection and wear control, material stability, part geometry and size, fixture rigidity, cutting parameters, and thermal control during cutting and measurement. For ultra-tight tolerances, clear communication on critical features, functional requirements, and inspection methods is important.
Surface Finishes and Post-Processing
Surface finish affects component functionality, assembly behavior, and corrosion resistance. Chinese CNC shops provide a wide range of as-machined and post-processed finishes for both metals and plastics.
As-Machined Surface Quality
As-machined surfaces from CNC milling and turning typically achieve Ra values between 1.6 and 6.3 μm, depending on tool path, feed rate, tool nose radius, and material. For precision parts that require low friction or improved sealing, a separate finishing operation (fine turning, polishing, or grinding) is added.
Metal Surface Treatments
Common metal finishing options include:
Bead blasting to create uniform matte surfaces, anodizing (Type II and hard anodizing) for aluminum to enhance wear and corrosion resistance, electroplating such as nickel, chrome, or zinc on steels and brass, powder coating for durable colored coatings, and black oxide for steel to reduce light reflection and mild corrosion protection.
Mechanical Finishing
Mechanical finishing operations such as deburring, vibratory tumbling, brushing, and polishing are widely used to remove sharp edges, burrs, and machining marks. Precision components may also receive manual deburring at critical edges and tight features to protect sealing surfaces and mating parts.
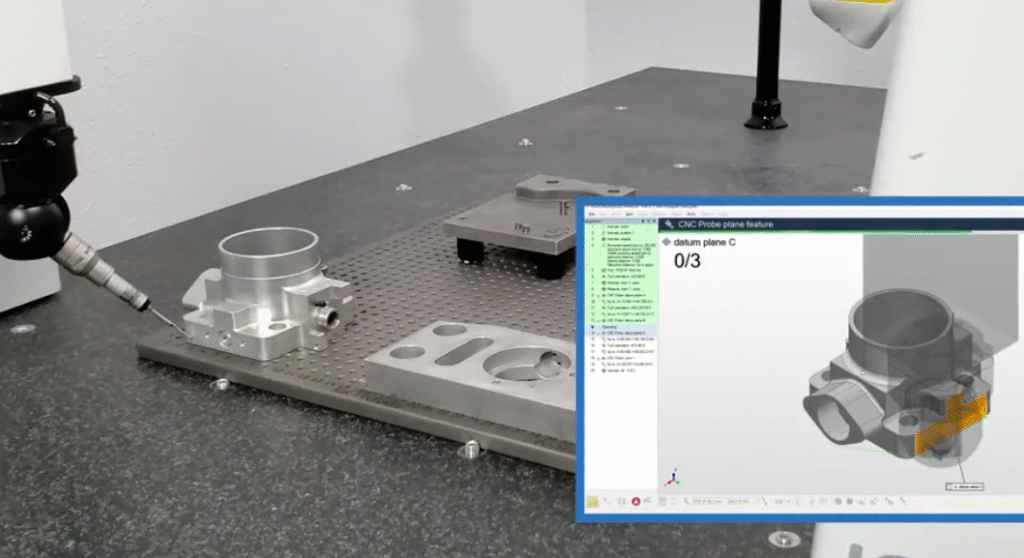
Quality Management and International Standards
Quality control in precision CNC machining in China is structured around international standards, documented procedures, and formal inspection processes. Many suppliers implement integrated quality management systems.
Quality Management Systems
Typical certifications and frameworks include:
ISO 9001 quality management systems for general industrial production, IATF 16949 for automotive-related manufacturing, ISO 13485 for medical devices, and AS9100 for aerospace components in advanced facilities. These systems govern document control, process audits, nonconformance handling, and continuous improvement.
Inspection and Metrology
Chinese precision machining shops often maintain a dedicated inspection room with controlled temperature, humidity, and calibrated equipment.
Common inspection instruments include:
Digital calipers, micrometers, height gauges, gauge blocks, plug and ring gauges, coordinate measuring machines (CMM) with touch probe or scanning heads, optical projectors, surface roughness testers, and hardness testers. Complex parts can be accompanied by full inspection reports, including material certificates, dimensional data sheets, and measurement records for specified critical dimensions.
Documentation and Traceability
Traceability is typically achieved through batch numbers and internal routing documents. For projects with higher requirements, suppliers can maintain traceability from raw material heat number through machining, heat treatment, finishing, and final inspection. This ensures that each part can be linked to specific process parameters and inspection results if needed.
Design Considerations for CNC Machining in China
Well-prepared designs reduce manufacturing risk, lead time, and cost. When working with Chinese suppliers, unambiguous documentation is essential.
Drawing and CAD Requirements
Most Chinese CNC shops accept 2D drawings in PDF, DWG, or DXF, and 3D CAD models in STEP, IGES, or other neutral formats. Drawings should clearly indicate:
Units (mm or inch), tolerances for critical and non-critical features, surface finish symbols, heat treatment requirements, and reference standards (such as ISO or ASME). Including 3D models helps clarify complex geometry, while 2D drawings define tolerances and functional relationships.
Dimensioning and Tolerance Strategy
A consistent tolerance strategy helps control cost while ensuring functionality. Overly tight tolerances across all dimensions increase machining and inspection time. A practical approach is to apply tighter tolerances only to critical features and interfaces and allow standard tolerances for non-critical dimensions.
Machinability and Feature Design
Designing for machinability improves both precision and efficiency. Typical considerations:
Specify internal corner radii rather than sharp corners to match tool diameters, allow adequate wall thickness to reduce deformation during machining, provide sufficient draft or clearance in deep pockets for chip evacuation and tool access, and avoid extremely thin ribs and deep narrow slots when not essential. When special features are unavoidable, they should be clearly highlighted as critical in the documentation.
Production Modes: Prototyping to Volume Manufacturing
Chinese CNC machining suppliers operate across a range of production scales, from one-off prototypes to large-scale recurring batches.
Rapid Prototyping and Short Runs
CNC machining is often chosen for prototypes and short runs when functional testing and material performance are important. With flexible programming and standard tooling, suppliers can deliver one-off parts and small batches with relatively short lead times, especially for aluminum and plastics.
Batch Production and Repeat Orders
For repeat orders and batch production, suppliers optimize tool paths, fixtures, and inspection routines. Dedicated jigs and fixtures improve repeatability, while process capability studies (e.g., Cpk) may be implemented for critical dimensions. Many factories manage blanket orders and scheduled shipments aligned with customer demand patterns.
Integration With Other Processes
CNC machining is frequently combined with other manufacturing processes such as die casting, investment casting, powder metallurgy, or sheet metal fabrication, where CNC is used for post-machining or finishing critical surfaces and interfaces. This hybrid approach balances cost efficiency with precision where necessary.
Working With Chinese CNC Machining Suppliers
Effective collaboration with Chinese suppliers involves clear technical communication, structured project management, and consistent quality verification procedures.
Supplier Capabilities Evaluation
When evaluating a CNC machining supplier in China, buyers typically consider:
Machine inventory and age, range of supported materials and part sizes, certification status, inspection equipment, historical experience with similar parts or industries, and responsiveness in technical communication. Factory visits or remote video audits can provide useful insight into process control and shop organization.
Communication and Technical Alignment
Clear technical communication minimizes misunderstandings and rework. Recommended practices include using unambiguous English technical terms, providing detailed drawings and models, specifying acceptance criteria and sampling plans in advance, and confirming critical features and reference surfaces. For complex parts, online meetings and annotated 3D models are often used to agree on machining strategies and inspection points.
Quality Assurance and Incoming Inspection
To align expectations, many buyers implement incoming inspection procedures upon receiving parts from China. This can include dimensional sampling, visual inspection for cosmetic features, verification of material certificates, and functional testing where applicable. Feedback loops with the supplier help fine-tune subsequent batches.
Typical Applications Across Industries
Precision CNC machining in China supports a broad range of industry-specific requirements.
Aerospace and Defense Components
These parts often require lightweight alloys (aluminum, titanium), complex 5-axis machining, and tight tolerances for mating surfaces and structural interfaces. Enhanced traceability and documentation are standard, and processes may be aligned with aerospace-specific quality frameworks.
Automotive and Transportation Parts
Automotive components include engine parts, drivetrain components, brackets, housings, and suspension hardware. Requirements focus on consistency, fatigue resistance, and cost-effective production at scale. For safety-related parts, stable process capability and robust QA documentation are emphasized.
Medical Devices and Equipment
Medical applications use stainless steel, titanium, and biocompatible plastics. Surface finish, cleanliness, and material traceability are critical. Typical parts include surgical instruments, orthopedic components, diagnostic equipment housings, and mechanical subassemblies.
Electronics, Robotics, and Industrial Equipment
Electronics and robotics demand precision housings, frames, fixtures, and motion components with accurate alignment and reliable mounting interfaces. Engineering plastics and aluminum are common for lightweight assemblies, while stainless steels and tool steels are used in high-wear environments.
Cost and Lead Time Considerations
Cost and lead time for precision CNC machining in China depend on material type, machining complexity, quantity, and finishing requirements.
Cost Drivers
Key cost drivers include part geometry complexity, tolerance tightness, material price and availability, requirement for multi-axis machining or special tooling, and the number of setups, fixtures, and inspections needed. When designing parts or preparing RFQs, providing prioritized tolerances and clear finishing specifications allows suppliers to optimize process routes and pricing.
Lead Time Planning
Lead time is influenced by manufacturing cycle time, heat treatment and surface finishing sequences, material procurement time, and shipping method. Sea freight requires longer planning horizons, while air freight reduces transit time at higher logistics cost. Coordination of engineering approvals, first article inspections, and batch production schedules is essential for stable supply.
Risk Mitigation and Practical Considerations
To ensure reliable outcomes when sourcing precision CNC machining in China, buyers can implement several practical measures.
Technical Risk Control
Using clear technical specifications, validated prototypes, and agreed inspection plans reduces risk. For function-critical components, it is common to approve a first article sample (FAI) before releasing larger volumes. Documenting change control procedures ensures that any modification in material, process, or design is formally reviewed and tested.
Logistics and Packing
Precision parts require appropriate packaging to avoid deformation, corrosion, or surface damage during transport. Chinese suppliers often use individual bagging, foam separators, and moisture protection. For sensitive surfaces, protective films and custom foam inserts help maintain cosmetic and dimensional integrity through long-distance shipping.