Hastelloy C-276 (UNS N10276, W.Nr. 2.4819) is a nickel-molybdenum-chromium superalloy with added tungsten designed for outstanding corrosion resistance in a wide spectrum of aggressive media. It is widely used in chemical processing, pollution control, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and power generation environments where both uniform and localized corrosion can rapidly cause failure in conventional alloys.
This guide presents a complete, technically focused overview of Hastelloy C-276, including composition, physical and mechanical properties, corrosion behavior, fabrication and welding guidelines, product forms, and typical industrial applications.
Overview of Hastelloy C-276 Alloy
Hastelloy C-276 is a wrought corrosion-resistant alloy in the Ni-Mo-Cr family. It was developed to handle strong oxidizing and reducing media, including hot contaminated acids and chloride-bearing environments, where many stainless steels, duplex grades, and even some nickel alloys do not offer sufficient reliability.
Key design features include:
- High nickel and molybdenum for resistance to reducing environments and pitting/crevice corrosion.
- Chromium for resistance to oxidizing media.
- Tungsten to further enhance resistance to localized corrosion.
- Low carbon and controlled silicon content to minimize carbide/silicide precipitation and intergranular attack.
Hastelloy C-276 is supplied primarily in the solution-annealed condition and is considered one of the most versatile corrosion-resistant alloys for severe service.
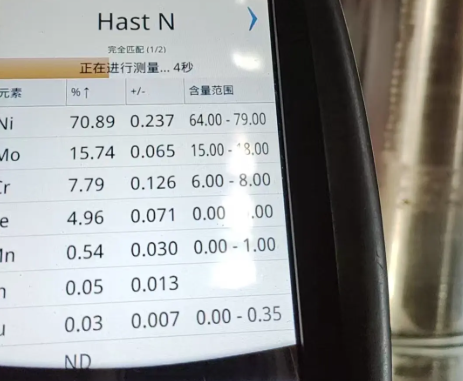
Chemical Composition of Hastelloy C-276
The carefully balanced chemistry of Hastelloy C-276 is fundamental to its performance in mixed acid and chloride-containing environments. The alloy is nickel-based with significant molybdenum and chromium contents, plus tungsten and controlled levels of iron and other elements.
| Element | Content (wt%) |
|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) | Balance (approx. 57–63) |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 15.0–17.0 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 14.5–16.5 |
| Iron (Fe) | 4.0–7.0 |
| Tungsten (W) | 3.0–4.5 |
| Cobalt (Co) | Up to 2.5 |
| Manganese (Mn) | Up to 1.0 |
| Vanadium (V) | Up to 0.35 |
| Silicon (Si) | Up to 0.08 |
| Carbon (C) | Up to 0.01 |
| Phosphorus (P) | Up to 0.04 |
| Sulfur (S) | Up to 0.03 |
The very low carbon and silicon levels reduce the risk of sensitization and intermetallic formation during fabrication, thereby maintaining excellent corrosion resistance after welding or thermal exposure within recommended limits.
Physical Properties of Hastelloy C-276
Physical properties of Hastelloy C-276 are relevant for design calculations, thermal analysis, and process equipment engineering.
- Density (at 20 °C): approximately 8.89 g/cm³
- Melting range: about 1325–1370 °C (2417–2498 °F)
- Electrical resistivity (at 20 °C): around 1.21 µΩ·m
- Thermal conductivity (at 20 °C): about 10–11 W/m·K
- Thermal expansion coefficient (20–100 °C): approx. 11.0–11.5 × 10⁻⁶ /K
- Modulus of elasticity (tension, at 20 °C): approx. 205 GPa
- Magnetic permeability: essentially non-magnetic in the annealed condition
These values are indicative and can vary slightly with product form and exact processing route. Design should be based on data from the relevant product specification or mill data sheet.
Mechanical Properties and Strength Data
Hastelloy C-276 provides a combination of good strength and high ductility along with its corrosion resistance. Mechanical properties depend on product form, thickness, and heat treatment, but typical values for solution-annealed plate or bar at room temperature are as follows:
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Ultimate tensile strength | ≈ 690–790 MPa | ≈ 100–115 ksi |
| 0.2% yield strength | ≈ 280–355 MPa | ≈ 40–52 ksi |
| Elongation (50 mm) | ≥ 40–50 % | ≥ 40–50 % |
| Reduction of area | ≈ 60 % | ≈ 60 % |
| Hardness (Brinell) | ≈ 200 HB max (typical 170–200) | ≈ 200 HB max |
At elevated temperatures, strength decreases as expected for solid-solution nickel alloys. For pressure vessel design, allowable stresses and temperature-dependent data should be taken from ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section II, Part D or equivalent design codes where Hastelloy C-276 is listed.
Corrosion Resistance Characteristics
Corrosion resistance is the primary reason for selecting Hastelloy C-276. It is suitable for a wide variety of aggressive environments and offers resistance to several modes of corrosion that can severely limit the service life of other alloys.
Resistance to General and Localized Corrosion
Hastelloy C-276 provides excellent resistance to uniform corrosion in both oxidizing and reducing media. It is particularly effective in:
- Hot hydrochloric, sulfuric, phosphoric, and acetic acids at a broad range of concentrations.
- Mixed acid environments, including those containing ferric and cupric ions.
- Seawater and brine systems where chlorides, hypochlorites, and other oxidizing species are present.
The alloy offers strong resistance to localized corrosion mechanisms, including:
– Pitting corrosion: The high molybdenum and chromium levels significantly increase resistance to pit initiation and growth in chloride-bearing solutions.
– Crevice corrosion: Tungsten in combination with Mo and Cr improves resistance to crevice attack, especially in high chloride or halide systems.
– Stress corrosion cracking (SCC): The alloy exhibits good resistance to chloride-induced SCC and to stress corrosion in many hot acidic environments where stainless steels quickly fail.
Behavior in Specific Corrosive Media
While exact corrosion rate data depend on temperature, concentration, and flow conditions, some general behaviors are widely recognized:
– Hydrochloric acid: Hastelloy C-276 is suitable for many HCl environments, including contaminated or aerated solutions, over a wide concentration and temperature range where most stainless steels and many nickel alloys are unsatisfactory.
– Sulfuric acid: The alloy performs well in sulfuric acid from dilute up to high concentrations, especially when chlorides or other contaminants are present. It is often chosen where carbon steel, stainless steel, and duplex stainless grades suffer rapid attack.
– Phosphoric acid: Good resistance in both pure and contaminated phosphoric acid, including wet-process phosphoric acid containing fluorides and chlorides.
– Nitric and oxidizing acids: Caution is required in strongly oxidizing systems such as high-temperature concentrated nitric acid, where Ni-Mo alloys are not ideal and alloys with higher chromium and lower molybdenum may be preferable. In many mixed acid conditions, however, Hastelloy C-276 remains an effective choice.
– Seawater and salt solutions: The alloy demonstrates high resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and SCC in natural seawater, brackish waters, and concentrated salt solutions, including under stagnant or low-flow conditions that are challenging for stainless steels.
– Chlorine-bearing environments: Good resistance to wet chlorine gas, hypochlorite solutions, and chlorine dioxide, making it suitable for bleaching and chlorination systems under controlled conditions.
Intergranular Corrosion and Welded Condition
Because Hastelloy C-276 is produced with very low carbon and silicon levels, it is less prone to sensitization and intergranular attack compared with older Ni-Mo alloys. When properly solution annealed and rapidly cooled, it maintains good resistance even after welding. Nevertheless, prolonged exposure in the temperature range that promotes carbide or intermetallic precipitation should be avoided if high corrosion resistance is required.

High-Temperature Performance and Oxidation
Hastelloy C-276 retains useful mechanical properties at moderately elevated temperatures. Typical applications include equipment operating up to about 400–500 °C (752–932 °F) in corrosive service. For higher temperatures, careful evaluation of both corrosion and mechanical behavior is required.
The chromium content provides resistance to oxidation and scaling in air or combustion gases at elevated temperature, but this is not primarily a high-temperature structural alloy. Where both high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance are needed, specific design data must be consulted.
In halide-containing or reducing environments at elevated temperature, corrosion behavior should be evaluated based on process-specific data, as service limits are highly dependent on the exact medium and operating conditions.
Heat Treatment and Microstructure
Hastelloy C-276 is supplied in a solution-annealed condition to achieve a homogeneous, single-phase matrix with optimal corrosion resistance and good formability.
Solution Annealing
Typical solution annealing parameters:
- Temperature: approximately 1120–1175 °C (2048–2147 °F).
- Holding time: sufficient for full heat penetration and dissolution of secondary phases (depends on thickness).
- Cooling: rapid cooling, typically water quenching or rapid air quenching, to avoid precipitation in the sensitizing temperature range.
After solution annealing, the microstructure is predominantly a single-phase solid solution with a fine grain size. This condition provides the best combination of corrosion resistance and ductility.
Stress Relieving and Post-Weld Heat Treatment
Stress relieving is generally not mandatory for Hastelloy C-276, as it has good resistance to stress corrosion cracking in many environments. However, when required for dimensional stability or high-stress applications, stress relieving is usually carried out at temperatures below the solution annealing range, with relatively short holding times.
Post-weld heat treatment is not always necessary and may not be practical for large fabrications. In many cases, components can be used in the as-welded condition, provided that appropriate filler metals and welding procedures are applied and that operating conditions do not promote intergranular attack.
Fabrication, Forming, and Machining
Hastelloy C-276 is a wrought alloy that can be formed and fabricated by common methods used for other nickel alloys. However, its high strength and work-hardening tendency require careful process planning and suitable tooling.
Cold and Hot Forming
Cold forming operations such as bending, deep drawing, rolling, and flanging are feasible. Key considerations include:
- Use of higher forming forces compared to austenitic stainless steels due to higher strength.
- Intermediate annealing when extensive deformation is required, to restore ductility and prevent cracking.
- Using generous bend radii where possible to reduce the risk of strain localization.
Hot forming is typically carried out in the temperature range of approximately 950–1175 °C (1742–2147 °F). For hot working:
– Ensure uniform preheating of the entire workpiece.
– Avoid working at too low a temperature, which can cause cracking, and at excessively high temperatures, which may lead to grain growth.
– Follow hot working operations by solution annealing and rapid cooling to restore corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Machining Characteristics
Hastelloy C-276 is more difficult to machine than low-alloy steels or stainless steels due to its high work-hardening rate and toughness. For efficient machining:
– Use rigid machine tools and setups to minimize vibration.
– Apply sharp, positive-rake cutting tools made of high-speed steel or, preferably, carbide grades suitable for nickel alloys.
– Use low cutting speeds, moderate feeds, and sufficient coolant to control heat and avoid surface hardening.
– Avoid tool dwell and rubbing; maintain continuous chip formation to reduce work-hardening of the surface.
Following these practices helps achieve good surface finishes and dimensional accuracy while optimizing tool life.

Welding and Joining of Hastelloy C-276
Hastelloy C-276 is readily weldable using standard methods suitable for nickel alloys. The alloy is typically welded to itself or to other corrosion-resistant alloys in process equipment, piping, and structural components.
Suitable Welding Processes
Common welding processes include:
– Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG): Preferred for thin sections and critical welds where high-quality, low-porosity weld metal is required.
– Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG): Used for thicker sections and higher productivity, often with appropriate shielding gases to control weld pool chemistry.
– Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW): Suitable for field welding and repair; requires low-hydrogen electrodes designed for Hastelloy C-276 or compatible compositions.
– Plasma arc and submerged arc welding can also be used with suitable consumables and parameters.
Filler Metals and Joint Preparation
For welding Hastelloy C-276 to itself, matching composition filler metals (commonly designated as Alloy C-276 filler wire or electrodes) are usually used to maintain corrosion resistance across the joint. When joining to dissimilar alloys, filler metal selection must consider the environment and galvanic effects.
Joint preparation involves:
– Thorough cleaning of the welding area to remove oils, grease, dirt, and oxides.
– Proper fit-up to minimize excessive heat input and distortion.
– Use of inert gas backing where needed to protect the root side from oxidation.
Control of Heat Input and Post-Weld Condition
Heat input should be controlled to limit grain growth and prevent formation of detrimental phases. Excessive interpass temperatures and slow cooling rates in the sensitizing temperature range should be avoided if high corrosion resistance is required.
In many chemical processing applications, Hastelloy C-276 welds perform well in the as-welded condition. For critical services, qualification testing such as corrosion testing of weld coupons may be specified.
Product Forms, Standards, and Specifications
Hastelloy C-276 is available in a wide range of wrought and fabricated product forms to support various design requirements in aggressive environments.
Common product forms include:
- Plate and sheet for vessels, tanks, linings, ducting, and structural components.
- Bar and forging stock for shafts, fasteners, fittings, and machined parts.
- Seamless and welded pipe and tube for process piping, heat exchangers, and instrumentation.
- Welding wire, electrodes, and filler metals for fabrication and repair.
- Flanges, elbows, tees, and other fittings for piping systems.
Typical standards and designations associated with Hastelloy C-276 include:
– UNS: N10276
– Werkstoffnummer: 2.4819
– ASTM specifications commonly covering Alloy C-276 products (examples, depending on product form):
• ASTM B575 for plate, sheet, and strip.
• ASTM B622 for seamless pipe and tube.
• ASTM B619 and B626 for welded pipe and tube.
• ASTM B574 for bar and forging stock.
• ASTM B366 for wrought fittings.
– ASME designations corresponding to the above ASTM standards for pressure equipment where applicable.
Specific project specifications may require additional testing or quality documentation, such as positive material identification, corrosion testing, or non-destructive examination.
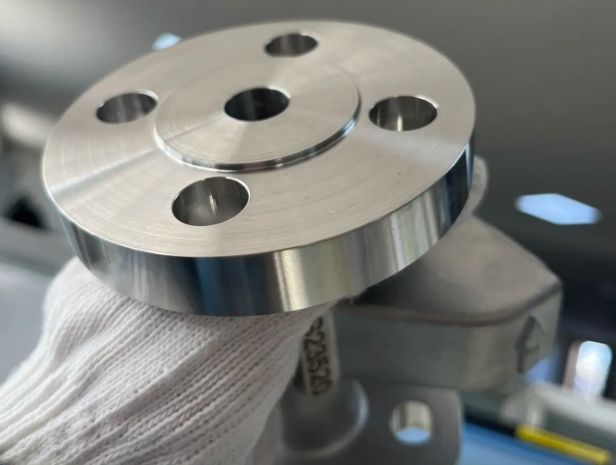

Industrial Applications of Hastelloy C-276
Due to its broad-spectrum corrosion resistance, Hastelloy C-276 is widely used in industries where equipment must withstand highly corrosive fluids, often at elevated temperatures and pressures.
Chemical Processing and Petrochemical Industry
In chemical and petrochemical plants, Hastelloy C-276 is frequently selected for:
– Reactors, agitators, and autoclaves handling strong acids, mixed acids, and chloride-laden media.
– Heat exchangers exposed to corrosive process streams on one or both sides, including tube sheets, tubes, and headers.
– Distillation columns, scrubbers, evaporators, and condensers in corrosive service.
– Transfer piping, valves, and fittings conveying aggressive chemicals.
Its ability to withstand both oxidizing and reducing conditions in the same system reduces the need for multiple materials and helps simplify design and maintenance.
Pollution Control and Waste Treatment
In environmental and pollution control systems, Hastelloy C-276 is used where flue gases, waste liquors, and slurries contain chlorides, sulfides, or other aggressive contaminants. Typical uses include:
– Flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems, including absorbers, ductwork, stacks, and dampers exposed to hot, acidic condensates and slurry.
– Components in incineration off-gas and scrubbing systems where halides and acids are present.
– Equipment in hazardous waste treatment and chemical waste neutralization facilities.
Pharmaceuticals, Food, and Fine Chemicals
Hastelloy C-276 is chosen in some pharmaceutical and fine chemical processes where highly corrosive intermediates or final products must be handled reliably. Applications include:
– Reactor vessels and accessories in multi-purpose plants processing aggressive chemistries.
– Filter housings, centrifuges, and dryers exposed to corrosive mother liquors.
– Transfer lines and valves where low contamination and high corrosion resistance are required.
While stainless steels are used widely in sanitary conditions, Hastelloy C-276 is applied where corrosion risk is beyond the safe limits of stainless grades.
Pulp and Paper Industry
In pulp bleaching and paper processing, strong oxidizing chemicals and chlorides can attack conventional materials. Hastelloy C-276 is used for:
– Components in chlorine dioxide and hypochlorite bleaching plants.
– Systems using peroxide, ozone, or other oxidizing agents in combination with chlorides.
– Piping and vessels for corrosive liquors at elevated temperatures.
Energy, Power Generation, and Other Uses
In power generation and related sectors, Hastelloy C-276 finds use in:
– Heat exchangers and condensers handling aggressive cooling waters or process liquids.
– Auxiliary systems in geothermal plants or other energy facilities where brines and corrosive fluids are present.
– Specialized nuclear and fuel processing systems where corrosion resistance and reliability are critical.
It is also used in marine and offshore environments for fittings and components exposed to seawater and sour service where standard stainless steels are inadequate.
Pain Points and Selection Considerations
While Hastelloy C-276 provides excellent technical performance in many corrosive environments, its selection should consider several practical aspects.
– Cost of alloy: As a nickel-based superalloy containing significant molybdenum and tungsten, Hastelloy C-276 is more expensive than most stainless steels and some other corrosion-resistant alloys. This drives careful optimization of wall thickness, component design, and use of cladding or linings where appropriate.
– Fabrication cost: Machining and forming are more demanding than for lower-alloy materials, which can result in higher fabrication costs and longer lead times. Specialized welding procedures and qualified welders may be required.
– Over-specification risk: In some processes, environments may not be severe enough to justify Hastelloy C-276, and alternative alloys (such as high-alloy stainless steels, duplex grades, or other nickel alloys) could be adequate. Proper corrosion testing and material selection studies help avoid unnecessary material cost.
– Availability and lead time: Although widely available, some sizes, product forms, or special conditions (e.g., heavy wall pipe, large forgings) may have limited stock and require mill production with associated lead times.
Due diligence in evaluating process conditions, failure history, and life-cycle cost allows engineers to determine whether Hastelloy C-276 is the most appropriate choice.
Handling, Inspection, and Maintenance
Correct handling and maintenance practices help ensure that Hastelloy C-276 components provide long service life in demanding environments.
– Handling: Avoid contamination of surfaces with iron particles or carbon steel tools that might lead to rust staining or galvanic effects. Use dedicated or properly cleaned tools when practical.
– Surface condition: For critical applications, finished surfaces may be pickled, passivated, or otherwise cleaned to remove fabrication oxides and residues, improving corrosion behavior.
– Inspection: Periodic inspection using visual examination, thickness measurement, and non-destructive testing helps detect early signs of corrosion or mechanical damage. Areas prone to crevice formation, deposits, or stagnant flow should receive particular attention.
– Maintenance: Where deposits or scaling occur, regular cleaning can reduce under-deposit corrosion risk. Any repairs should be carried out with compatible filler metals and qualified welding procedures to maintain corrosion resistance.
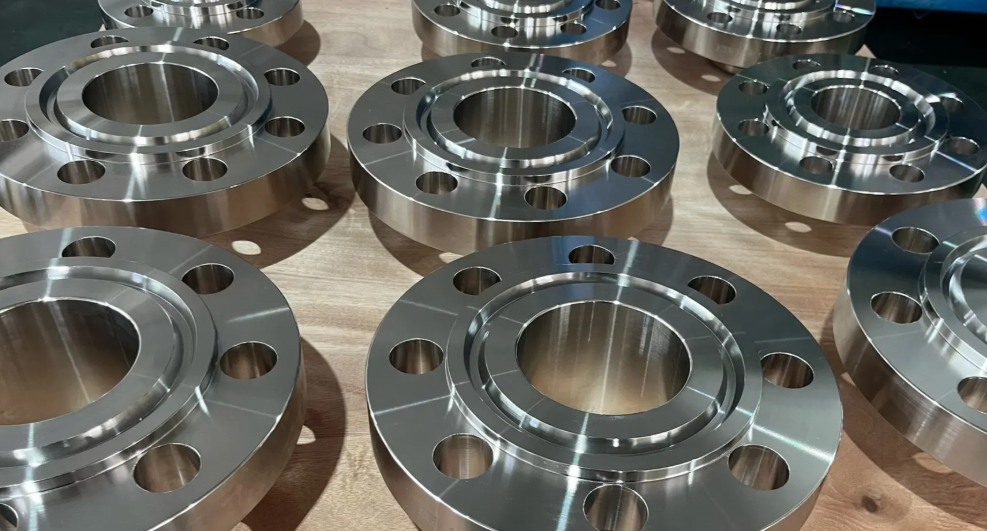

Summary and Engineering Benefits
Hastelloy C-276 is a widely established nickel-molybdenum-chromium alloy offering a rare combination of resistance to both oxidizing and reducing environments, including many media that are contaminated or mixed. Its strengths include:
– Excellent resistance to a wide range of acids and chlorides, including hot, contaminated solutions.
– Strong resistance to localized attack such as pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking in many environments.
– Robust performance in welded condition when proper procedures and filler metals are used.
– Availability in a broad range of product forms suitable for pressure vessels, piping, heat exchangers, and complex process equipment.
These characteristics make Hastelloy C-276 a reliable material for critical components in chemical processing, pollution control, pharmaceuticals, pulp and paper, and various energy-related industries, where failure due to corrosion is not acceptable. When selected and fabricated correctly, it contributes to long equipment life, reduced unplanned downtime, and improved plant safety in some of the harshest service conditions.
XCM Machining – Making Hastelloy C-276 Easy to Control
Hastelloy C-276 is famous for being “difficult to machine” — but with XCM, it becomes stable, predictable, and production-ready. Leveraging our experience in high-nickel alloys, we optimize tools, parameters, and cooling strategies to deliver tight tolerances, consistent surface finish, and longer tool life on every C-276 part. Choose XCM, and turn your Hastelloy C-276 machining from a cost burden into a competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hastelloy C-276
What is Hastelloy C-276?
Hastelloy C-276 is a nickel-molybdenum-chromium alloy known for its exceptional resistance to corrosion, especially in harsh chemical environments. It performs well in both oxidizing and reducing conditions.
What are the main advantages of Hastelloy C-276?
Key advantages include excellent resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, stress corrosion cracking, and strong acids such as sulfuric and hydrochloric acid. It also maintains strength at elevated temperatures.
Is Hastelloy C-276 difficult to machine?
Yes. Hastelloy C-276 is considered difficult to machine due to its high strength, rapid work hardening, and poor thermal conductivity. Specialized tooling, slower cutting speeds, and experienced machining practices are required.
How does Hastelloy C-276 compare to Inconel?
Compared to many Inconel alloys, Hastelloy C-276 offers superior resistance to a broader range of corrosive chemicals, while Inconel alloys are often chosen for higher temperature and high-strength applications.
Is Hastelloy C-276 suitable for high-temperature applications?
Yes. Hastelloy C-276 retains good mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for high-temperature and high-corrosion environments, though it is primarily selected for corrosion resistance rather than extreme heat strength.


