CNC milling services are widely used for producing precise, repeatable parts from metals, plastics, and other materials. By combining computer control with multi-axis cutting tools, CNC milling delivers high dimensional accuracy and consistent surface quality for prototypes and production runs.
What CNC Milling Services Are and How They Work
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from a solid workpiece. The cutting tool movement and spindle speed are controlled by a CNC program, typically generated from a 3D CAD model through CAM software.
The basic workflow for CNC milling services is:
- CAD model creation or import
- CAM programming and toolpath generation
- Material selection and workholding setup
- Machine setup (tools, offsets, zero points)
- Milling operations (roughing, semi-finishing, finishing)
- Inspection, deburring, and secondary operations if needed
Service providers may operate vertical machining centers (VMCs), horizontal machining centers (HMCs), and 5-axis mills, allowing flexible part orientations and complex geometries.

Core Capabilities of CNC Milling Services
CNC milling services cover a wide range of operations and performance characteristics. Understanding these capabilities helps you align part designs and requirements with the right supplier.
Common Milling Operations
Typical CNC milling operations include:
- Face milling for creating flat surfaces and accurate heights
- Peripheral milling for profiles, slots, and shoulders
- Pocket milling for internal cavities and recesses
- Drilling, tapping, reaming, and countersinking holes
- Contouring for 2.5D and 3D profiles
- Thread milling for internal and external threads with high accuracy
Many CNC milling services combine multiple operations in a single setup to reduce handling, improve accuracy, and shorten lead times.
Axis Configurations and Part Complexity
CNC milling machines are classified by the number of controllable axes:
3-axis: X, Y, and Z linear axes. Suitable for planar features, pockets, and profiles accessible from the top or a limited number of re-clamp orientations.
4-axis: Adds rotational motion (typically around the X or Y axis), allowing machining of multiple sides without manual repositioning. Useful for cylindrical parts, features around a circumference, and improved productivity.
5-axis: Adds two rotational axes, enabling the tool to approach the part from many angles. This supports undercuts, complex freeform surfaces, and high-precision features in a single setup, reducing tolerance stack-up and setup time.
Tolerances, Accuracy, and Repeatability
CNC milling services can reach tight tolerances when the machine, fixtures, environment, and inspection are properly controlled. Typical commercial service ranges are:
| Feature Type | Common Tolerance Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| General linear dimensions | ±0.05 mm to ±0.10 mm | Standard for many prototypes and non-critical components |
| Precision linear dimensions | ±0.01 mm to ±0.02 mm | Requires stable process, high-quality machines, and inspection |
| Hole diameters (reamed/boring) | ±0.005 mm to ±0.02 mm | Depends on hole size, tool type, and depth |
| Flatness/parallelism | 0.01 mm to 0.05 mm per 100 mm | Affected by part size, material, and clamping |
| Surface location (true position) | 0.02 mm to 0.20 mm | Used in GD&T; depends on overall datum scheme |
Actual achievable tolerances depend on material, part size, feature geometry, and the service provider’s equipment and quality control processes.
Surface Finish Characteristics
CNC milling generates characteristic tool marks and surface roughness values (Ra). Common ranges are:
• Roughing passes: Ra 3.2–6.3 μm (125–250 μin), suitable for non-critical surfaces.
• Standard finishing: Ra 1.6–3.2 μm (63–125 μin), widely used for functional components.
• Fine finishing or finishing with specialized tooling: Ra 0.8–1.6 μm (32–63 μin), used for mating surfaces or partially cosmetic areas.
For very smooth or decorative surfaces, secondary processes such as grinding, polishing, or coating are typically applied after milling.

Materials Supported by CNC Milling Services
CNC milling services support a broad material spectrum, enabling suitable combinations of strength, weight, cost, and performance for different applications.
Metals
Metals are the most common materials in CNC milling due to their strength, thermal resistance, and structural properties.
Typical metals include:
Aluminum alloys: 6061, 6082, 7075, 2024 and others. They combine high machinability, good strength-to-weight ratio, excellent thermal conductivity, and relatively low cost. Frequently used in aerospace, automotive, consumer products, and enclosures.
Stainless steels: 303, 304, 316, 17-4 PH. Selected for corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and cleanliness. Suitable for food processing equipment, medical devices, marine hardware, and structural components.
Carbon steels: e.g., 1018, 1045. Provide good strength and hardness after heat treatment, but require surface protection (plating, painting) against corrosion in many environments.
Tool steels: D2, A2, O1, H13, and others. Used for molds, dies, and wear-resistant components due to high hardness and dimensional stability after heat treatment.
Copper alloys: Copper, brass, bronze. Offer high electrical and thermal conductivity or specific tribological properties. Used in electrical connectors, heat sinks, and decorative components.
Titanium alloys: e.g., Ti-6Al-4V. Offer a combination of high strength, low density, and corrosion resistance. Machining is more demanding, often requiring optimized cutting strategies, rigid setups, and appropriate tooling.
Plastics
CNC milling services also process engineering plastics for lightweight and chemically resistant components.
Common plastics are:
ABS and polycarbonate (PC) for housings, fixtures, and prototypes.
PA (nylon), POM (acetal), and HDPE for wear components, gears, and sliding parts.
PEEK, PPS, and other high-performance plastics for high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments.
Machining plastics requires attention to clamping pressure, heat generation, and chip evacuation to avoid deformation, melting, or poor surface finish.
Other Materials
Some CNC milling services can handle:
• Composites (e.g., carbon fiber laminates) with suitable dust extraction and tooling.
• Casting blanks that require machining of critical surfaces and features.
• Soft materials like modeling boards for fixtures, gauges, or patterns.
Design Considerations for CNC Milled Parts
Designing with CNC milling in mind helps reduce cost, improve manufacturability, and maintain quality. Certain geometries and features are more efficient to produce than others.
Geometry and Feature Design
Key points for design include:
Internal corners: Milling tools are round, leaving internal radii. Sharp internal corners require very small tools, increasing cost and time. Adding reasonable corner radii that match standard cutter sizes improves efficiency.
Wall thickness: Extremely thin walls increase risk of vibration, deflection, and breakage. Maintaining minimum practical wall thickness (often > 0.8–1.0 mm for metals and > 1.5–2.0 mm for plastics, depending on size) improves stability.
Feature depth: Deep pockets or holes increase tool deflection and wear, sometimes requiring multiple tool lengths or specialized strategies. Whenever possible, limiting depth or redesigning to shorter features can be beneficial.
Undercuts: Some undercuts can be produced with T-slot or lollipop cutters, but they increase setup complexity. If frequent undercuts are required, 5-axis capability or alternative manufacturing processes may be considered.
Tolerancing and GD&T
Applying realistic tolerances is critical. Overly tight tolerances increase cost significantly due to slower feeds, more tool changes, additional inspection, and potential scrap. Efficient use of GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) can clarify functional requirements without over-constraining non-critical features.
Best practices include:
• Concentrating tight tolerances on critical interfaces.
• Using datums that reflect real assembly conditions.
• Communicating tolerance priorities to the service provider.
Workholding and Accessibility
Workholding strongly influences feasibility and cost. Features that are difficult to reach from any orientation may require multiple setups or special fixtures. Considering the following during design can simplify workholding:
Provide flat clamping surfaces or features for vice or fixture gripping.
Limit features that require extremely long tools or awkward approach angles.
When possible, design parts so that most features are accessible within one or two primary orientations.
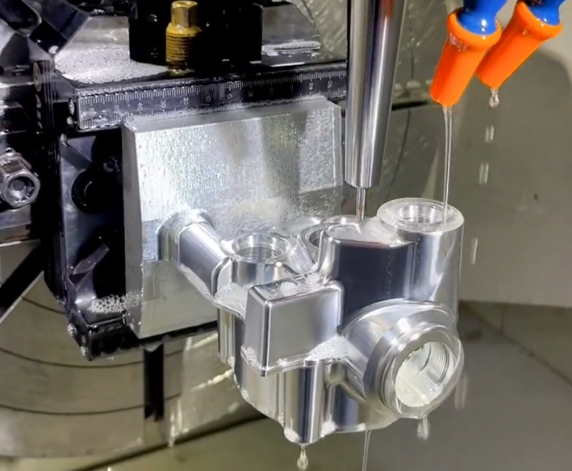
Benefits of Using Professional CNC Milling Services
Professional CNC milling services provide multiple advantages for both prototypes and production parts, beyond what is achievable with manual machining or less capable equipment.
Precision and Repeatability
CNC milling enables consistent dimensional accuracy across multiple parts. Once a process is validated, the same program can be reused, ensuring repeatable results. This is essential for interchangeable parts, assemblies, and long-term production runs.
Scalability from Prototype to Production
CNC milling services can support a complete product life cycle:
Rapid prototypes: Short-run machining from CAD data with minimal tooling cost allows quick design verification.
Bridge production: Low to medium volumes can be produced while tooling for other processes (e.g., casting, molding) is still under development.
Full-scale production: For some applications and volumes, CNC milling remains the primary method due to its flexibility and relatively low changeover cost.
Material and Finish Flexibility
CNC milling services allow switching between materials and surface finishes with fewer constraints than many other processes. This flexibility is beneficial when optimizing for strength, cost, corrosion resistance, or appearance.
Typical secondary finishes offered include anodizing, plating, painting, powder coating, bead blasting, and engraving, allowing functional and cosmetic customization.
Reduced Lead Times and Consistent Quality Control
Modern CNC milling services use standardized workflows, digital quoting, and integrated quality control to shorten turnaround times. Many parts can be delivered in days rather than weeks, depending on complexity and finishing requirements.
Quality control often includes:
Incoming material verification, in-process measurement, final inspection, and documentation such as inspection reports or material certificates when requested.
Cost Structure of CNC Milling Services
The cost of CNC milling is influenced by multiple technical and commercial factors. Breaking down the main cost elements helps in controlling budget and optimizing design.
Calculate Your CNC Milling Cost
Enter the details below to calculate the estimated cost for CNC milling.
Key Cost Drivers
Major contributors to CNC milling cost include:
Material cost: Determined by material grade, size of stock, and yield from the raw block or bar.
Machine time: Driven by cutting volume, toolpaths, required tolerances, and surface finishes. Complex features and tighter tolerances generally require longer machining time.
Setup time: Includes programming, fixturing, and initial machine setup. For low quantities, setup can represent a significant portion of overall cost.
Tooling and consumables: Tool wear is affected by material, cutting parameters, and required surface finish. Special tools or custom fixtures add additional cost.
Secondary operations: Deburring, finishing, heat treatment, and inspection beyond standard checks can add to the overall price.
Cost Behavior with Order Quantity
CNC milling costs typically behave as follows with increasing quantity:
| Quantity Range | Cost Characteristics | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 1–10 parts | High unit cost due to setup and programming; flexible design changes | Prototypes, engineering validation, spare parts |
| 10–100 parts | Setup cost spread over more units; potential for fixture optimization | Pilot runs, low-volume products, custom components |
| 100–1,000 parts | Lower unit cost; may justify dedicated fixtures and optimized toolpaths | Bridge production, specialized assemblies, industrial equipment |
| 1,000+ parts | Further reduced unit cost when process is highly optimized; evaluation of alternative processes may be appropriate | Ongoing production, standardized components |
Cost Optimization Considerations
To control CNC milling costs, engineers and buyers often consider:
Relaxing non-critical tolerances and surface finish requirements.
Redesigning to reduce deep pockets, very thin walls, or very small features.
Using standard material sizes to improve material utilization.
Combining similar parts in a single order to share setup costs.
Typical Applications of CNC Milling Services
CNC milling services are used across industrial, commercial, and consumer sectors for both functional and structural parts.
Industrial and Mechanical Components
Applications include brackets, housings, frames, manifolds, base plates, and precision fixtures. These parts often require robust mechanical properties, precise alignment, and compatibility with other components in assemblies.
Aerospace and Automotive
In aerospace and automotive applications, CNC milled parts are commonly used for structural components, mounting brackets, engine and drivetrain parts, and complex housings. Material selection and traceability, along with tight tolerances and documentation, are often critical.
Medical and Laboratory Equipment
Medical and lab applications use CNC milled components made from stainless steels, titanium, and engineering plastics. Examples include instrument housings, surgical instrument components, clamps, and custom lab fixtures, where cleanliness, precision, and material compatibility are essential.
Electronics and Consumer Products
Electronics housings, heat sinks, mounting plates, and mechanical interfaces are frequently CNC milled from aluminum or plastics. For consumer products, appearance and surface finish, as well as dimensional consistency, tend to be significant requirements.
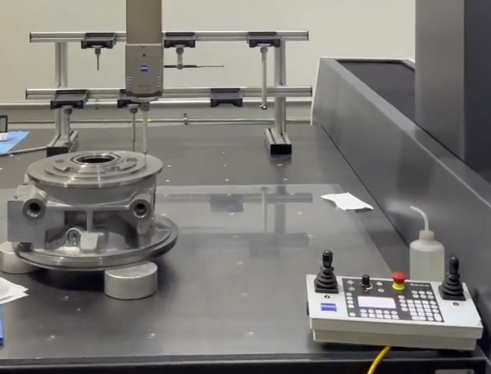
Selecting a CNC Milling Service Provider
Choosing a suitable CNC milling service provider involves evaluating technical capabilities, quality systems, communication, and logistics. A structured approach can reduce risk and improve project outcomes.
Technical Capability and Equipment
Key aspects include:
Machine types and axis capability: Availability of 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis machines; spindle power; maximum travel ranges; and ability to handle your part size.
Material expertise: Experience with the specific metals or plastics required, especially for more difficult materials like titanium, hardened steels, or high-performance polymers.
Inspection equipment: Use of coordinate measuring machines (CMM), optical measurement, surface roughness measurement, and material testing when required.
Quality Systems and Documentation
Reliable CNC milling services typically operate under structured quality systems. Consider whether the provider can offer:
Process control and documented work instructions.
Material traceability, certificates, and lot tracking.
Inspection reports, first article inspection (FAI), and other documentation as needed.
Communication, Lead Time, and Support
Effective communication supports manufacturable design and predictable lead times. Consider:
Clarity and responsiveness of quotations, including detailed breakdown of materials, machining, and finishing.
Support for design for manufacturability (DFM) feedback to refine features, tolerances, and material choices.
Lead time commitments and capacity for urgent or repeat orders.
Cost vs. Capability Balance
Lowest price is not always the most cost-effective option if it compromises quality, lead time, or risk. A balanced evaluation considers:
Supplier’s track record and references.
Stability of quality across multiple orders.
Overall value in terms of precision, delivery reliability, and support.
Common Issues and How CNC Milling Services Address Them
When sourcing machined parts, companies often face recurring issues. Well-organized CNC milling services typically address these through process control and clear communication.
Dimensional Inconsistency Across Batches
Variation between batches can cause assembly problems and rework. Professional CNC providers reduce this risk through standardized setups, documented offsets and tool libraries, and consistent inspection practices.
Long Lead Times for Design Changes
Product iterations may require frequent design updates. CNC milling services that use digital workflows, updated CAD/CAM integration, and flexible fixtures can implement design revisions faster, reducing time to market.
Limited Visibility into Cost Drivers
Without clarity on cost contributions from material, setup, and machining, optimization is difficult. A transparent service provider can indicate which features or requirements are cost intensive, enabling targeted design adjustments and more predictable budgets.

XCM CNC Milling Services — Accuracy, Speed, Reliability
XCM delivers high-precision CNC milling services designed to meet the demanding requirements of modern manufacturing. With advanced multi-axis equipment, experienced engineers, and strict quality control, we machine complex metal and plastic components with exceptional accuracy and consistency. From rapid prototyping to full-scale production, XCM helps global customers reduce lead times, control costs, and bring high-quality parts to market faster.
When CNC Milling Services Are a Good Fit
CNC milling services are particularly suitable when you require:
Precise, repeatable components with defined geometries and tolerances.
Moderate lead times and flexibility in materials and design changes.
Low to medium production volumes or bridge production before high-volume tooling.
Access to a broad set of metals and plastics, with optional secondary finishes.
For parts with simple geometry, very high volumes, or special requirements, other processes such as stamping, die casting, injection molding, or additive manufacturing may be alternatives. However, CNC milling remains a widely applicable and technically robust option for many applications.
FAQ
What information is needed to get a CNC milling quote?
Typical data required includes a 3D CAD model (and 2D drawing if tolerances and finishes are critical), material specification, quantity, surface finish requirements, special tolerances or GD&T, and any required certifications or inspection documents. Providing this information upfront allows for accurate pricing and lead time estimates.
What capabilities are included in CNC milling services?
CNC milling services typically include 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis machining, tight-tolerance cutting, complex geometry processing, drilling, tapping, slotting, and surface finishing for both metal and plastic parts.
What are the main benefits of CNC milling services?
Key benefits include high precision, repeatability, design flexibility, fast turnaround times, and suitability for both prototyping and production manufacturing.
How accurate are CNC milling services?
Modern CNC milling services can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.002 mm, depending on material type, part geometry, and machining conditions.
What factors influence the cost of CNC milling services?
Costs are affected by material selection, part complexity, machining time, tolerance requirements, surface finishes, order quantity, and setup complexity.


