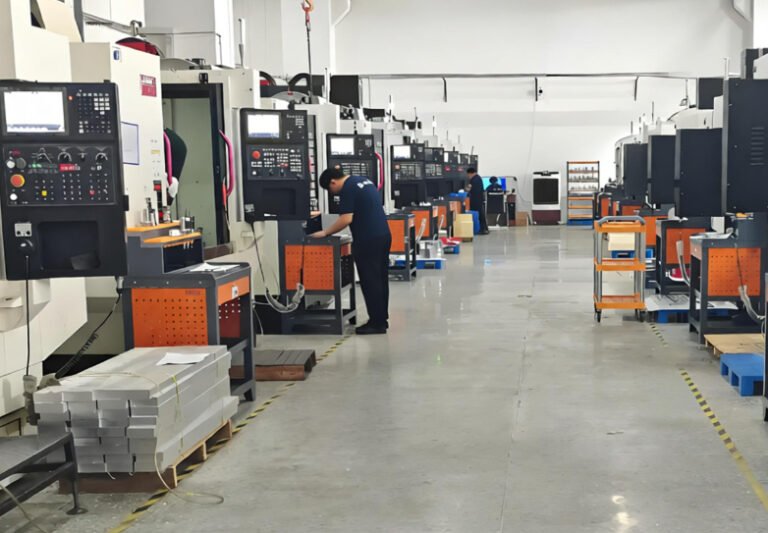
Overview of CNC Machining in China
China has become a major global source for CNC machined components, serving industries such as automotive, aerospace, robotics, medical devices, consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and custom machinery. Chinese CNC machine shops offer a wide range of subtractive manufacturing processes with competitive pricing and scalable production capacity.
Most production is concentrated in manufacturing hubs such as Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shandong. These regions combine dense supplier networks, extensive raw material availability, and mature logistics systems, enabling short lead times from prototype to mass production.
Chinese CNC machining services typically support end-to-end workflows: design for manufacturability review, programming, machining, inspection, surface finishing, assembly, and packaging for export. The supply base ranges from small job shops to large, ISO-certified factories equipped for high-volume, multi-shift operation.
Core CNC Machining Capabilities in China
Chinese machine shops cover a broad portfolio of CNC processes suitable for rapid prototypes, functional samples, and large production runs.
CNC Milling
CNC milling is widely available, from basic 3-axis vertical machining centers to more advanced 4-axis and 5-axis machines. Common applications include housings, brackets, fixtures, manifolds, structural components, and precision plates.
- 3-axis milling for simple prismatic parts and general purpose machining
- 4-axis milling for parts requiring rotary operations or multiple side features
- 5-axis milling for complex geometries, organic shapes, and multi-face machining in a single setup
Typical milling work-envelope ranges and spindle speeds are suitable for aluminum, steels, and engineering plastics. Many shops also integrate pallet changers and automated tool changers to improve throughput.
CNC Turning and Turn–Mill
CNC turning is widely used for shafts, bushings, fittings, fasteners, and rotational components. Chinese suppliers operate slant-bed lathes, bar feeders, and twin-spindle, live-tooling turn–mill centers.
Turn–mill machines enable completion of complex rotational parts with milled flats, grooves, holes, and threads in a single setup. This reduces handling and improves consistency for medium to high-volume production.
Multi-Axis Machining
5-axis and simultaneous multi-axis machining are increasingly used for parts requiring intricate contours, undercuts, and tight tolerances across multiple faces. These capabilities are important in sectors such as aerospace components, medical implants, molds, and high-precision tooling.
Suppliers with multi-axis capability often support advanced CAM programming, fixture design, and process optimization to minimize cycle time while maintaining accuracy.
Auxiliary Machining Services
Many Chinese CNC suppliers integrate secondary processes for complete part production:
- Wire EDM and sinker EDM for sharp internal corners and hard materials
- Grinding (surface, cylindrical, centerless) for fine surface finishes and precision fits
- Tapping, reaming, and broaching for holes and internal profiles
- Laser engraving or marking for logos, serial numbers, and part identification
These integrated services reduce the need for multiple vendors and simplify logistics.
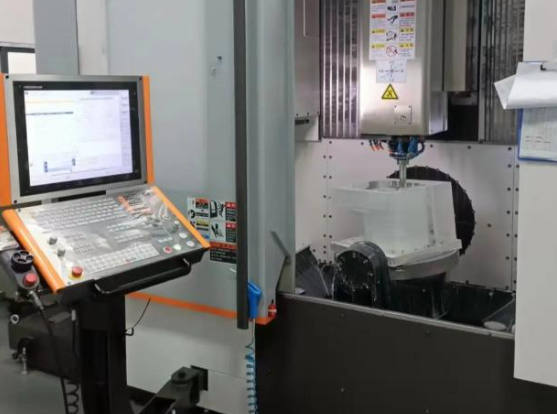

Supported Materials and Their Typical Uses
China CNC machining services support a broad range of metals and plastics, making it possible to match material properties to specific functional and environmental requirements.
| Material Category | Representative Grades | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | 6061, 6082, 7075, 2024, 5052 | Enclosures, brackets, structural parts, heat sinks, fixtures, custom profiles |
| Carbon Steel | Q235, 1018, 1045, 20#, 45# | Shafts, bases, gears (pre-hardened), machine components, welded assemblies |
| Alloy Steel | 4140, 4340, 40Cr, 42CrMo | High-strength components, tool holders, drive components, heavy-duty parts |
| Stainless Steel | 304, 316, 316L, 303, 17-4PH | Food-grade parts, medical hardware, corrosion-resistant fittings, instrumentation |
| Copper & Brass | H59, H62, C3604, C110 | Electrical connectors, fluid fittings, decorative hardware, thermal components |
| Titanium Alloys | Ti-6Al-4V (TC4), TA2 | Medical implants, aerospace components, high strength-to-weight parts |
| Tool Steel | D2, SKD11, H13, P20 | Molds, dies, cutting tools, wear-resistant inserts |
| Engineering Plastics | POM (Delrin), PA (Nylon), PC, ABS, PEEK, PTFE | Gears, bushings, insulation components, housings, prototypes |
Material sourcing is frequently done through established domestic distributors. Many shops can provide material certifications (e.g., mill test reports, RoHS, REACH, or specific chemical composition analysis) when required by the buyer.
Tolerances, Accuracy, and Surface Finish
China CNC machining suppliers regularly produce parts with industrial-grade tolerances suitable for assemblies, jigs, fixtures, and functional prototypes. Precision-focused factories support higher accuracy through controlled processes and advanced equipment.
| Parameter | Common Capability | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| General dimensional tolerance | ±0.10 mm | Standard non-critical features on most metals and plastics |
| Precision dimensional tolerance | ±0.02–0.05 mm | Achievable on many CNC mills and lathes with appropriate fixturing |
| High-precision tolerance | ±0.005–0.01 mm | Possible on select machines for specific features with detailed requirements |
| Hole position tolerance | ±0.05–0.10 mm | Depends on hole size, pattern, and inspection method |
| Surface roughness (Ra) – as-milled | Ra 1.6–3.2 μm | Standard finish for most structural parts |
| Surface roughness (Ra) – fine machining / grinding | Ra 0.4–0.8 μm | Used for bearing surfaces, sealing surfaces, and precision fits |
Tolerances are normally based on ISO 2768 or customer-specified drawings. For tight tolerances or critical features, it is important to clearly mark them on 2D drawings and communicate inspection requirements in advance.
Surface Treatments and Finishing Options
China’s manufacturing ecosystem offers wide access to surface finishing services that can be combined with CNC machining for both functional and aesthetic purposes.
Metal Surface Treatments
Common finishing processes for metals include:
- Anodizing (Type II and hard anodizing): aluminum parts, color and wear resistance
- Electroplating: nickel, chrome, zinc, tin for corrosion protection and appearance
- Powder coating: durable, uniform coating in various colors and textures
- Passivation: stainless steel corrosion resistance enhancement
- Black oxide: low-cost black finish for steel components
- Phosphate coating: improved paint adhesion and corrosion resistance
Mechanical and Cosmetic Finishes
Chinese suppliers also support purely mechanical finishing such as:
Bead blasting, sand blasting, polishing, brushing, deburring, and tumbling are widely used to remove sharp edges and achieve consistent cosmetic appearance for consumer products and exposed assemblies.
Production Volumes and Lead Times
China CNC machining services support the full spectrum from one-off parts to long-term, high-volume production contracts.
Typical volume scenarios include:
Single prototypes and small batches for design validation and testing. Medium batches (hundreds to a few thousand pieces) for pilot runs and low-volume production. Larger batches (tens of thousands of parts) for mature products with stable demand.
Lead times depend on part complexity, finishing requirements, and factory workload. For simple prototypes without special surface treatment, machining lead times of 3–7 days are common after order confirmation. For production orders with multiple processes, lead times of 2–5 weeks are typical, excluding international shipping. Buyers often negotiate framework agreements and buffer inventory for critical components to ensure continuity of supply.
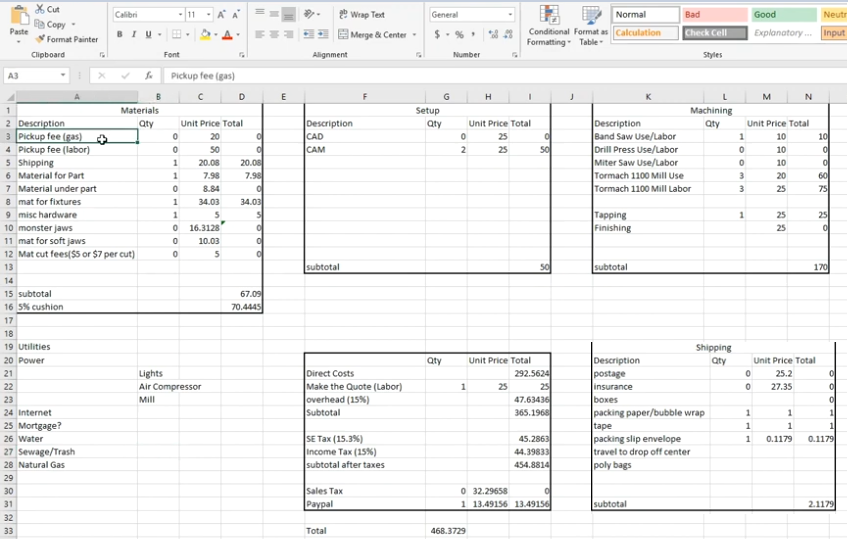
Cost Structure of CNC Machining in China
China is often selected for CNC machining due to competitive pricing. Cost advantages come from labor rates, supply chain integration, and high equipment utilization. Understanding cost structure helps buyers optimize designs and negotiate effectively.
Key Cost Components
Overall part cost usually consists of:
Setup and programming cost, reflecting CAM programming, fixture design, and machine setup time. Machining time, determined by cutting strategy, material, and required tolerances. Material cost, driven by grade, stock dimensions, and yield from raw material. Tooling and consumables, including cutting tools, inserts, and fixtures. Secondary processing and finishing, such as heat treatment, coating, and assembly. Inspection and quality documentation, especially when detailed reports or certificates are required. Packaging and logistics for internal transport and export shipment.
Factors that Influence Pricing
Common pricing drivers include:
Part geometry complexity and number of setups. Tolerance level and surface finish requirements. Material hardness and machinability. Batch size and repeat order potential. Required lead time (standard vs. expedited production). Volume forecasts and long-term cooperation expectations.
Calculate CNC Machining Cost in China
Chinese suppliers often adjust unit prices significantly when volumes increase, especially once programming and fixturing costs are amortized over multiple batches.
Quality Control Practices in Chinese CNC Shops
Quality control capability in China ranges from basic dimensional checks to comprehensive inspection systems. Many export-oriented factories maintain structured quality management systems.
Quality Management Systems
Common certifications include ISO 9001 for general quality management, and for specific sectors, ISO 13485 (medical devices) or IATF 16949 (automotive) in some factories. Certification status should be verified by requesting copies of certificates and checking their validity with the issuing bodies.
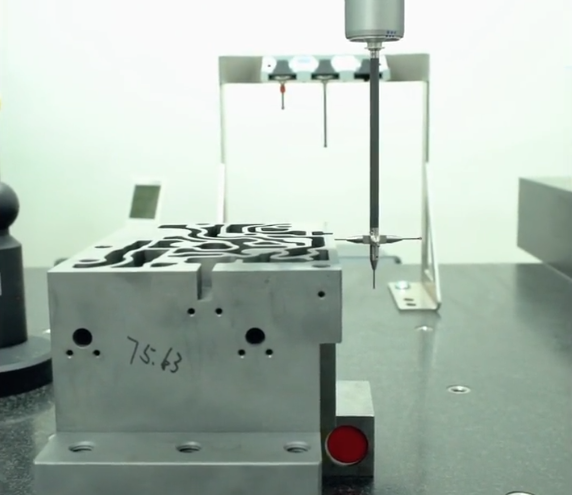
Inspection Equipment
Typical measurement equipment found in Chinese CNC shops includes:
Calipers, micrometers, height gauges, and plug gauges for basic dimensional checks. Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) for 3D feature inspection on critical parts. Optical projectors and microscopes for detailed feature verification. Surface roughness testers for Ra measurements. Hardness testers (Rockwell, Brinell, Vickers) for material hardness verification.
Process and Final Inspection
Inspection is usually performed at multiple stages:
Incoming material inspection to check certificates and basic properties. In-process inspection to control critical dimensions during machining, often by operators or in-line QC staff. Final inspection with sampling or 100% inspection for critical components, with measurement reports prepared when requested.
Buyers can specify sampling plans (e.g., AQL levels) and require inspection reports in agreed formats to match internal quality systems.
Design Data, Drawings, and Communication
Successful CNC projects rely on clear technical communication. Chinese suppliers commonly work with a combination of 3D models and 2D engineering drawings.
Accepted File Formats
Standard file formats include:
3D CAD: STEP (preferred), IGES, Parasolid, STL for reference geometry. 2D drawings: PDF, DWG, DXF for dimensions, tolerances, and notes.
Drawing and Specification Practices
2D drawings should clearly define:
Critical dimensions and tolerances, with reference to standard tolerance systems if applicable. Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) when necessary for position, flatness, parallelism, and other geometric controls. Surface finish requirements and any critical surface zones. Material grade, hardness or heat treatment, and any specific material standards. Surface treatments and color codes for anodizing, powder coating, or plating. Inspection requirements, sampling plans, and documentation expectations.
Clear drawings minimize ambiguity, reduce the risk of rework, and support consistent inspection on both sides.
Order Process and Typical Workflow
The order process with Chinese CNC machining suppliers usually follows a structured sequence from RFQ to shipment.
Quotation and DFM Review
Buyers send 3D models, 2D drawings, quantity requirements, and any special notes. The supplier evaluates machinability, risks, and cost; some suppliers perform a basic Design for Manufacturability review and may suggest adjustments to radii, wall thickness, or tolerances for better process stability or lower cost.
Sample and Pilot Runs
For new parts, a sample or small pilot batch is typically produced before full-scale production. The buyer reviews physical samples, verifies fit and performance, and may request dimensional reports on critical features. Feedback from this stage is used to finalize process parameters and quality checkpoints.
Mass Production and Logistics
Once samples are approved, mass production begins according to the agreed delivery schedule. The supplier manufactures, inspects, and packs components for export. Shipping is usually arranged by sea freight for large volumes or air freight / express for smaller or urgent shipments. Commercial documents such as packing lists, invoices, certificates of origin, and inspection reports accompany the shipment as required.
Issues and Practical Considerations
When working with China CNC machining suppliers, buyers may encounter specific pain points that require proactive management.
1) Dimensional Interpretation and Tolerance Assumptions
When drawings include incomplete or ambiguous tolerancing, suppliers may apply default tolerance systems that do not match the buyer’s expectations. This can lead to parts that are technically within the supplier’s standards but not fully compatible with the buyer’s assemblies.
Clearly specifying tolerances, especially for mating features and hole patterns, and aligning on applicable standards reduces this issue.
2) Surface Finish and Cosmetic Expectations
Cosmetic standards, especially for visible consumer parts, can vary between customers and suppliers. Descriptions such as “good cosmetic finish” are interpreted differently.
Defining measurable parameters (e.g., Ra values where relevant), using reference samples, and documenting acceptable blemish criteria support consistent results.
3) Batch Consistency Over Time
Maintaining identical quality across multiple batches and repeat orders requires stable processes and documented setups. Without this, slight changes in tooling, fixtures, or operators may introduce variation.
Requesting that suppliers retain process documentation, setup records, and inspection data for repeat parts helps maintain batch-to-batch consistency.
Intellectual Property and Data Security
When sending CAD files to Chinese suppliers, protection of proprietary designs is an important consideration. While many export-oriented factories work with international customers and understand confidentiality requirements, practices still vary.
Buyers commonly use Non-Disclosure Agreements specifying that drawings, models, and parts cannot be shared with third parties. Some buyers split assemblies across multiple suppliers to reduce the exposure of full product designs. Others provide simplified models where detailed internal features are not necessary for machining.
Clear contractual terms and selecting suppliers that show established IP management practices contribute to better control of design information.
How to Evaluate and Select a China CNC Supplier
Choosing a suitable CNC machining partner in China involves technical, quality, and commercial evaluation steps.
Technical Fit
Evaluation includes checking whether the supplier’s equipment and experience match the complexity and tolerances of your parts. Requesting machine lists, material experience, and sample part photos can help assess capabilities. Suppliers with in-house finishing or strong networks with surface treatment providers are advantageous for parts requiring multiple processes.
Quality and Reliability
Quality evaluation covers certifications, inspection equipment, and process control. Buyers often ask for sample inspection reports, quality manuals, and descriptions of internal QC procedures. Trial orders and on-site or third-party factory audits provide additional insight into real production practices and consistency.
Communication and Responsiveness
Efficient communication is important for resolving technical questions and handling engineering changes. Response time, clarity of feedback, and willingness to discuss technical details indicate how smoothly collaboration will proceed. English-language capability and stable contact persons facilitate long-term cooperation.
Commercial Terms
Commercial assessment includes pricing, payment terms, lead times, and incoterms. Common payment structures involve deposits before production and balance before shipment or against shipping documents. Clear agreements on delivery schedules, liability for non-conforming parts, and rework or replacement policies should be established in writing.
Applications of China CNC Machining Across Industries
China CNC machining supports both standard and highly specialized components in multiple sectors.
In automotive applications, Chinese suppliers produce brackets, housings, drivetrain components, and test fixtures. In aerospace and defense, selected certified factories machine structural parts, mounts, and precision hardware according to strict material and documentation requirements. Consumer electronics and hardware products rely on precisely machined aluminum enclosures, knobs, and internal mechanical elements. Medical and laboratory equipment manufacturers source precision manifolds, instrument components, and small stainless steel or titanium parts from qualified Chinese shops.
Industrial equipment builders use China CNC machining services for gears, shafts, frames, and custom mechanical assemblies, leveraging the combination of machining, welding, and finishing available in local supply chains.
Logistics, Packaging, and Export Documentation
International shipments from Chinese CNC suppliers generally follow standard export procedures.
Packaging Practices
Parts are usually protected with foam, bubble wrap, or custom trays, then packed in inner boxes and outer cartons. Heavier components may be packed in wooden crates or pallets meeting international shipping requirements. Rust-preventive oils, papers, and desiccants are used for corrosion-sensitive metal parts during sea transport.
Shipping Methods and Documentation
Buyers can select air freight, express courier, or sea freight depending on volume and urgency. Common incoterms include EXW, FOB, and CIF. Export documentation typically consists of commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading or airway bill, and, when needed, certificate of origin, material certificates, and inspection reports.
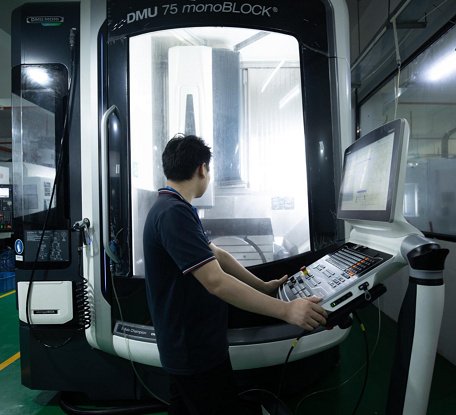

XCM — Advanced CNC Capabilities, Competitive Costs, Reliable Quality
At XCM, we combine advanced CNC machining capabilities, including multi-axis milling and turning, with cost-efficient manufacturing processes and strict quality control systems. From prototypes to high-volume production, we deliver precision-machined parts that meet international standards. With transparent pricing, stable lead times, and experienced engineering support, XCM is your trusted CNC machining partner in China for reliable, high-quality manufacturing solutions.
FAQs about China CNC Machining
What is China CNC machining?
China CNC machining refers to precision machining services provided by CNC machine shops in China, using computer-controlled equipment to produce custom metal and plastic parts with high accuracy and repeatability.
Is CNC machining in China reliable?
Yes. Many CNC machining manufacturers in China operate under strict quality management systems such as ISO 9001 and use advanced inspection equipment to ensure consistent quality for international customers.
Is China CNC machining cost-effective?
Yes. China CNC machining is generally cost-effective due to efficient production processes, skilled labor, and economies of scale, while maintaining competitive quality standards.
How do I ensure quality when sourcing CNC machining from China?
Quality can be ensured by reviewing supplier certifications, requesting samples, confirming inspection reports, and maintaining clear communication on specifications and tolerances.


